Nov-2020
- Assertion (A): Concurrent validity coefficients are generally higher than predictive validity coefficient
- Reason (R) : This does not mean that the test with higher validity coefficient is more suitable for a given purpose
- Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
- Performance test – Concurrent validity – Extent of agreement between two measures – Analysis of the meaning of test scores for the purpose it was constructed
- Aptitude test – Predictive validity – Measure of product or performance – Students are not allowed unlimited time to respond to all questions.
- Personality test – Construct validity
- Achievement test – Content validity
- Which method of the qualitative research focuses on language and meanings that are given to texts, for the purpose of creating and shaping knowledge and behaviour?
- a) Discourse analysis (2) Narrative research (8) Trend analysis (4) Grounded theory
- The sampling methods which are probability based
- Cluster sampling
- Quota sampling
- Systematic sampling
- Dimensional sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Match the types of research in List I with the features in List II.
- Exploratory – Qualitative data is gathered first and the same predominates later
- Cross-sectional – Macro level analysis attempted for the data
- Explanatory – Quantitative data is gathered first and the same predominates later
- Triangulation – Quantitative and qualitative data are gathered and integrated
- Longitudinal – Retrospective analysis of history of a unit helps to interpret remembered information.
- But time consuming and expensive as it involves the influences of various factors like the interaction of biological, environmental and intervention.
- Which among the following is best suited for assessment of social skills?
- a) Checklist (2) Rating scale (3) Numerical scale (4) Rubrics
- A: Raising the level of significance increases the possibility of committing type II error
- R: Higher level of significance increases the probability of rejecting the true hypothesis(research hypothesis)
- (A) is false but (R) is true.
- On rejecting null hypothesis, the mean of control and treated cannot be same.
- If null hypothesis is rejected when it is true, it indicates – Type I error.
- If there is a significant difference between control and treated, researcher tends to reject the null hypothesis.
- Identify from the list of characteristics given below those which are related to a good hypothesis in a research :
- Simplicity of explanation
- Plausibility of explanation
- Highly difficult to verify the postulated relations
- Not related to an existing theory
- Relationship formulated among variables having conceptual clarity
- A teacher finds that the distribution of scores for a self made test is positively skewed. What inference he/she should make about the difficulty level of this test?
- The test is difficult
- The test is easy
- The test is of moderate difficulty
- The test is moderately of low difficulty.
- In a negatively skewed curve obtained after testing students, the correct inference about the difficulty of the test would be
- The test was easy – The majority of students score high marks in a test.
- In a negatively skewed curve obtained after testing students, the correct inference about the difficulty of the test would be
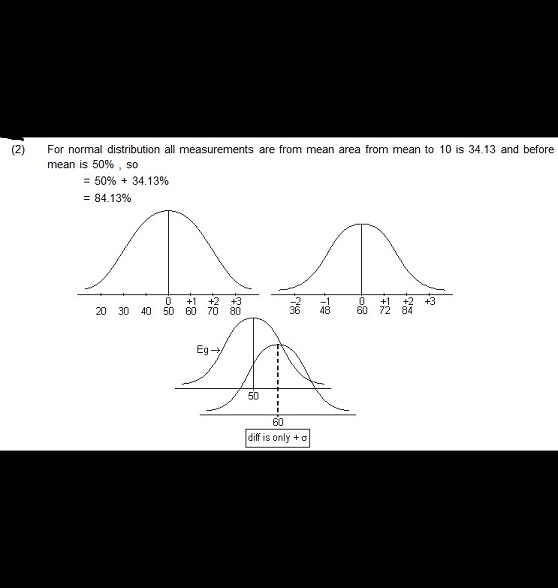
- A university teacher has conducted a survey of achievement of students in chemistry through a self made test. The distribution of scores has been studied in terms of mean and standard deviation for a sample of 100 students. The results are as follows Mean = 50 Standard deviation = 10 and N = 100. Assuming that the distribution of scores is normal. what will be the Percentile Rank (PR) of a student whose score is 60?
- 70 2) 75 (3) 80 (4) 84
- Z- score measures how many SD away from the mean
- The standard deviation of the z-scores is always 1.
- The graph of the z-score distribution always has the same shape as the original distribution of sample values
- 50+34.13 = 84.13 for 1 S.D+1/2 normal dbn curve
- 70 2) 75 (3) 80 (4) 84
- Given below is a summary of ANOVA for four groups of students tested in a research project.
| Source of variance | sum of squares | Degree of freedom | Mean sum of squares |
| Between groups | 76 | 3 | 23.33 |
| Within groups | 122 | 16 | 7.62 |
- What will be the value of ‘F for the above data?
- (1) 76/122 (@) 3/16 (3) 23.33/7.62 (4) 7.62/23.33
- Assertion (A): Tests with larger number of items have higher reliability
- Reason (R): Each test item adds to test reliability
- (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
- Identify the sequence in generating a grounded theory
- Deciding about the needed sampling design and data collection
- Coding and memoing
- Categorization and comparison
- Identification of the core variable leading to its saturation
- Theory verification and generalization emerging
- After cleaning of collected data research coding is essential
Dec-2019
- What is the correct sequence of actions in conducting an intervention-based action research in Education?
- Plan, act, observe and reflect
- An investigator wants to study the functioning of a school meant for tribal children. The most appropriate research design for this context would be classified as Ethnography.
- In a research study the variable which is not directly observable but whose effect is inferred on the dependent variable is termed as Intervening variable.
- Which of the following statement are true from reliability of a research tool?
- It is correlation of scores on the testing tool itself
- It varies from sample to sample
- It is affected by variance of scores.
- Which of the following research designs is the most appropriate for depicting lived experiential realities?
- Phenomenological designs
- On the basis of Flanders’ Interaction Analysis Categories (FIAC) in a 10 x 10 observation matrix, the cells which indicate a sustained level of verbal interchange are known as Steady State Ratio (SSR).
- In which of the following, the main purpose of research is to formulate generalizations leading to theory building?
- Experimentation with controls and manipulation of variables.
- Which of the following statements are true for a historical research design?
- Mostly based on qualitative data
- Data are examined for validity and authenticity
- Content-analysis is used for data treatment.
- An investigator commits type Il error when he/she accepts a null hypothesis when it is false.
- A weighing machine mostly over measures the weight of individuals. It will be said to be indicative of Systematic Error.
- Which of the following are the assumptions underlying the use of parametric statistics:
- The variable being studied is continuous
- Scores are normally distributed
- Variances over all groups are equal
| Parametric | Non-parametric |
| The variable being studied is continuous(nominal/ordinal) | used for Interval data |
| Scores are normally distributed | distribution-free statistics – Methods that do not use any assumptions. |
| Variances over all groups are equal. Eg. Independent t-test, ANOVA F-test | Variance differ for each sample so to calculate mean sum of squares. Eg. chi-square test, ANCOVA |
- In the process of drawing a random sampling which of the following process is in order of sequence?
- Define target population, decide sample size, list all the units of target population and drawing the sample by randomization.
- the correct order of measurement scales in increasing order of accuracy, precision and number of operations used Nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio.
- Which of the following research designs utilizes data from individuals,autobiograpies and personal talks/discussions Narrative research design
- The combination of different approaches to validate information,
- strategies, and results in a research study is technically known as Triangulation.
- It is an attempt to map out or explain the richness and complexity of human behavior by studying it from more than one standpoint, using both quantitative and qualitative data.
June-2019:
- In a research study, the effect of three independent variables such as gender, socioeconomic status of the family and locus of control on scholastic performance in social studies was to be ascertained. The dependent variable was measured using an interval scale. Which of the following statistical techniques will be considered appropriate for this data?
- ‘F’ test
- A researcher gives two tests-one English language and another in Mathematics. He/She find the mean and standard deviation of each of the two groups n = 100, as follows :
- English Mathematics
- Mean 50 60
- Standard deviation 10 12
- Assuming the curve for the two distributions overlapping, how many students in English language are below the mean of those in Mathematics?
- (1) 34 (2) 84 (3) 16 (4) 32
- Assuming the curve for the two distributions overlapping, how many students in English language are below the mean of those in Mathematics?
- In which of the following modes of testing, a student is given optimum scope for displaying his/ her accomplishment?
- Power test
- In a testing survey of class X student with N = 500, their mean was observed as 80 and standard deviation as 8. Assuming normality of distribution of their scores, how many students would be below the score of a student getting 88?
- 421
- From the list given below, identify the statements which appropriately describe the main characteristics of steps in scientific method :
- Identifying and defining the problem
- Formulating hypothesis
- Collecting, organizing and analyzing data
- Formulating conclusions
- Verification, rejection or modification of the hypothesis
- What is the distinctive feature of case study research?
- Developing on in-depth understanding of the case
- The following represents the distinctive feature of qualitative research
- Perspective based, inductive and meaning giving
- In randomly constitute two groups experimental and control, a researcher obtains the following results after using a parametric ‘t’ test :
- Value of t = 3 for N = 300
- On the basic of this evidence which decision in respect of substantive research hypothesis and the null hypothesis will be justified ?
- Rejecting the null hypothesis and accepting the research hypothesis
- A researcher intends to study the adjustment problems of students who are slum dwellers. What should be the sampling procedure used for such a study?
- Cluster sampling
- A school teacher plans a research study to find out the relationship between level of aspiration and socio-economic status of students’ parents. Which type of research design will be appropriate for this study?
- Non-experimental research design
Dec-2018:
- List I (Characteristic of Validity Measure) List II (Type of Validity)
- Measure of product or performance – predictive validity
- Measure of unobservable – Construct validity
- Measure of representation of substantive knowledge structure – Content validity
- Extent of agreement between two measures – concurrent validity.
- Given below are two statements, one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct answer using the code given below.
- Assertion (A) :Homogeneous tests have low reliability
- Reason (R) :Range of test scores affects reliability.
- Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- The shape of the curve showing the distribution of percentile ranks is rectangular.
- Unlike a normal distribution of scores, which are bell shaped, the distribution of percentile ranks is uniform and is rectangular in shape.
- As percentile scores are not normally distributed, One shouldn’t compute means and standard deviations of percentile scores

- An investigator conducted a study to examine the effect of gender on attitude towards dowry system. The nature of this study was Causal comparative.
- List I (Types of variable) List II (Correlation coefficient)
- Both variables continuous – Pearson’s r
- Both with ordinal measure – Spearman’s rho artificial dichotomy
- Both with artificial dichotomy – Tetrachoric r
- One continuous and other with artificial dichotomy – Biserial
- Two or more categories – Contingency coefficient
- Match Types of research are given in List I and their descriptions in List II
- True experimental research – Cause-effect relationship between manipulated conditions and measured outcome
- Evaluation research – Judging the worth of a particular practice
- Basic research – Concerned with theory building and explaining natural phenomena
- Applied research – Exploring the possibility of use of theory in varied situations
- Eg. The effect of peer learning is studied in relation with achievement and motivation.
- An example of a distal method in Educational Psychology is Ex-post facto method
- The mean and standard deviation of a set of scores are 43 and 8 respectively. If each raw score is decreased by 5, the new mean and standard deviation would be (38, 8)
- An investigator used ANOVA to compare four groups of students numerical ability on the basis of a test. After analysis of raw scores, the following resulting were obtained :
- Source of Variation df Sum of Squares
- Between Groups 3 625.00
- Within Groups 36 2128.00
- Mean sum of squares,
- 625/3 = 208.33 and 2128/36 = 59.11
- F-ratio = 208.33/59.11 = 3.52
- The value of F-ratio would be approximately : 3.52
- Mean sum of squares,
- In ethnographic research, a researcher uses a non-interactive strategy, which describes people’s experiences and connotes their feelings. Which of the following strategies does it refer to ?
- Artifact collection
- An investigator used t-test to compare two groups of students on verbal aptitude. He repeated his experiment 20 times and obtained significant difference 19 times. On the basis of this he decided to reject the null hypothesis. The probability of committing type I error was
- 0.05
- Null hypothesis is true, since there is a significant difference 19 times.
- But rejecting it gives rise to type 1 error at Alpha 95%
- so decreasing alpha from 0.05 to 0.01 the power of statistical test decreases.
- After which research hypothesis becomes directed to achieve the purpose intended for researcher.
- 0.05
- In a normal distribution of scores with a mean of 54 and standard deviation of 9, the percentile rank of a student scoring 72 would be 48
- 34.13+13.59 = 47.72 approx 48
- Which of the following measures is used for describing the units of differences from the central tendency measure such as mean ? Standard deviation
- In a class test, the mean for Psychology was 45 and SD was 5, while for Maths the mean was 80 and SD was 5. Mr. Bipin Kumar gets 50 marks in Psychology and 70 marks in Maths. In which subject will he be considered to have done better ?
- He has done better in Psychology.
- Which of the following methods of reliability of a test describes the average correlation of all split half correlations and can be applied when there are more than two options to each item ?
- Cronbach’s alpha
- An investigator obtained a correlation coefficient of + 0.65 between two variables. The other investigator obtained a correlation coefficient of – 0.65 between the same variables. Which of the two values indicates a higher degree of relationship ?
- Both indicate the same degree of relationship
- Which of the following statements about reliability of a test are correct ?
- It is a correlation of the test with itself.
- It varies from sample to sample.
- A teacher prepares a list of latest arrivals in the various libraries of the colleges of a university. His list reflects the number of books as reported. Which of the measurement scales is implied in this ?
- Ratio
- A school principal gave a spelling test to 256 students. The distribution of scores was found to be normal with a mean of 42 and standard deviation of 8 points. The probability is 0.95 that the mean of corresponding population would be less than the upper limit of
- 42.98
- X=42
- Z value of 0.95% =1.96
- SD=8 and n= 256
- X+-Z*SD/ root N
- =42+- 1.96*8/root 256
- 42+-1.96*8/16
- 42+-0.98 SO, upper limit = 42.98
- 42.98
- A test was given to 360 students of Class X and a normal distribution of scores was obtained. The mean of scores was 45 with a standard deviation of 9points. The percentage of students who scored outside the limits of scores 36 – 54 would be
- 32
- % of students who scored outside the limits of scores 36-54 would be -1Z to 1Z = 16 + 16 = 32%
- 100-(34.1%+34.1% ) = 32%
- 32
July-2018:
- Categories of Tests are given as Set-I and their description as Set-II.
- (a) Standardized test – developed by experts, administered and scored by using an objective procedure
- (b) Norm referenced test – used for comparing individuals in terms of their relative position
- (c) Diagnostic test – analysis of strength and weakness of students for further help
- (d) Criterion referenced test – Raw scores are compared with some pre-determined standard
- In a negatively skewed curve obtained after testing students, the correct inference about the difficulty of the test would be
- The test was easy.
- A multiple choice test consists of 50 test items. The difficulty values of items vary in a narrow range with an average value of 0.48. The test gave variance of 81 when administered to a group of students. The reliability co efficient of the test would be 0.86.
- The percentile rank of a student on a test was found to be 67. This means that 67% students scored below his score.
- A test having 20 items has a reliability coefficient of 0.60. If 80 more similar items are added, the new reliability coefficient would be : 0.86
- Reliability coefficient cannot be negative as its based on the reliability of the test
- r n(new reliabiity) = r0(old reliabiityy) * k(Number of times) / 1+(k-1)*r0
- = 0.6*4/1+(4-1)*0.6 = 2.4/2.8 = 0.86
- Using equivalent samples, a researcher obtained a significant correlation 95 times out of 100 trials. He/She decided to reject the null hypothesis. The alpha level would be 0.05.
- Which of the following term is closely related to the meaning of the term aptitude?
- Potential
- If the deviation of a score from the mean is given as 10 and standard deviation as 5, what will be the T-score for the concerned raw score ? 70
- T-score = 50 + (X-M/SD) * 10
- x-m = 10, SD = 5
- T = 50+(10/5) * 10 = 70
- A teacher prepares a test for measuring socially acceptable behavior of participants in the school program. What type of reliability would be considered to be important ?
- Inter-rater reliability
- While assessing the attitude of administrators towards a women empowerment programme, a researcher had no preconceived notions about what she might discover, and she continued interviewing until key themes emerge. Indicate the paradigm of research being followed :
- Grounded theory approach
- A group of 10 students was randomly drawn from Class 12 and was given yoga training for three weeks. Their wellness life style was compared with another similarly selected group which did not undergo such training. Which type of statistical test will be appropriate for testing the tenability of Null Hypothesis ?
- Independent t-test
- Which of the following decisions will tend to decrease sampling error ?
- Obtaining representative sample
- When you read a research article published in a journalwhich is not peer reviewed, what aspect of the report should you be most concerned about ?
- rigour reflected in reporting the research
- Set-I (Approaches to sampling in qualitative research) Set-II (Characteristics)
- Extreme case sampling – Seeks cases that are unusual
- Purposive sampling – Seeks cases according to his/her judgement about the appropriateness
- Snowball sampling – Seeks help from participants to identify additional participants
- Set-I Set-II
- Nominal Scale – Listing students according to participation in Co-curricular activities
- Ordinal Scale – Ranks of the students in a musical test
- Interval Scale – Intelligence scores on a Verbal test
- Ratio Scale – Speed of students in writing words per minute
- For estimating maximum value of multiple correlation,which of the following conditions should be met ?
- I. Independent variables should correlate high with the dependent variable.
- II. The Independent variables should correlate low withone another
- Both conditions I and II should be met
- The application of Multivariate ANOVA (MANOVA) justifies
- More than one dependent variable with moderate inter correlations have been employed
- A method of sampling that ensures proportional representation of all sections of a population is technically called Stratified Sampling.
- Two variables X and Y have a negative correlation coefficients of n = 48. The proportion of variance common to both the variables will be : 0.23.
- In a sample distribution with N = 300, M = 60 and SD= 12, the number of cases falling above the score 48 will be 252
- Z = X-M/SD
- Z=48-60/12 =-1
- Percentile rank at -1z =16%
- % of cases falling above the score 48 = 100-16 = 84%
- No. of cases falling above the score 48 = 300*84/100 = 252
- Sampling Distribution of mean is normally distributed with respect to the type of population distribution and size of samples
- So, SD of sample dbn of mean is less than the SD of population Dbn.
- If the population distribution is normal, then the sampling distribution of the mean is likely to be normal for the samples of all sizes
- If two variables X and Y have significant negative correlation, which of the following statement is true ?
- X and Y vary together
- A college librarian plans the purchase of books keeping in view the demand of different books among students. Which of the following measures of central tendency would be suitable for this purpose ?Mode
- An investigator wants to conduct a study to ascertain the progress of implementation of RTE Act-2009. Which of the following research tools would be most suitable for this purpose ? Questionnaire
- A researcher used t-test to compare two means based on independent samples and found the t-value to be significant at .05 level. This means that:
- The t-value to be significant means the Chances are 5 out of 100 that the difference between means has occurred due to sampling errors.
- A researcher uses both t-test and F-test on the same data obtained from two groups. The functional relationship between values of t and F if calculated would be :
- t^2= F
- Below are given two sets of statistical tests of significance. Set-I lists the parametric tests while Set-II provides their non-parametric counterparts.
- Independent t-test – Mann Whitney U test
- Dependent t-test – Willeoxon T-test
- ANOVA F-test – Kruskal Wallis H-test
- one way ANOVA for independent samples – Friedman’s ANOVA
- Which of the following tools at a Guidance Centre can be used for ascertaining prospective success in a chosen occupation ?
- Differential Aptitude test
Non-Parametric vs Parametric tests:
- The measurement of an entire population yields Parameter.
- For use of a non-parametric test like the chi-square the following assumption has to be satisfied.
- No assumption about the nature of distribution is required.
- However, the following are allowed for non-parametric test
- data cannot be arise from interval measures(nominal or ordinal)
- distribution cannot be normal
- cannot be dichotomous variables.
- Good conditions for holding non-parametric test:
- No assumption about the properties of the population
- Methods that do not use distributional assumptions
- Use of data that are not obtained as interval or ratio measure
- General assumptions of parametric test
- normal probability and
- control of variables
- A researcher conducts a yoga training camp to see its effect on wellness lifestyle of participants. In post training session he/she assess the change having taken place in the level of wellness. The proposition valid for statistical test to be carried out is
- Parametric value of H1 is greater than the parametric value of H0.
- Which combination of the following conditions holds good for non-parametric tests ?
- No assumptions about the defining properties of the population.
- Methods that do not use distributional assumptions.
- Uses of data that are not obtained as interval or ratio measure.
- In research situations, non parametric statistics is used for Interval data
- parametric – Nominal, Ordinal.
- The correlation coefficients that can be considered as non-parametric in nature Rank difference correlation.
- To evaluate whether the item of MCQ’s significantly discriminates between the Low scoring and High scoring groups.
- Significance of difference between two groups can be tested by
- T- test and F-test
- A teacher researcher has obtained data from a questionnaire used for teacher and head teachers in the from of a contingency table of 3 ×3 for anxiety and awareness levels. Which statistical test will indicate whether the two variables are interdependent?
- Chi-square test
Miscellaneous:
- A research hypothesis
- is more specific than a problem statement
- is supported or not supported by theory
- Relates variables that can be measured, manipulated and categorized.
- is not a statement including the participants of the study
- is not the same as statistical hypothesis.
- In a research formulation, ” the more the adolescents are expose to social media the lower their levels of academic achievement likely to become
- In the statement of hypothesis independint variable is exposure to social media
- The most appropriate statistics the researcher may use in the process of standardisation of multiple choice test, while doing analysis to test the hypothesis for each item response.
- Chi square test
- The association among variables in a scientific study is indicated quantitatively as coefficient.
- A: Reliability coefficient cannot be negative
- R: Reliability is based on the correlation of the test itself
- Both A and R correct it is the correct explanation of A
- Phenomenological research = Immersion, incubation, illumination, explication, creative synthesis
- an investigator used two matched groups to compare the effectiveness of two methods of teaching science. this is causal comparative study
- Research for exploring the applicability of a theory or law formulated in a specific situation in the field of education is termed as Applied research
- As a researcher you want to evaluate the teaching performance of a teacher. Most appropriate tools rating scale
- When the population is homogenous the random sampling technique is more appropriate
- List-1 test and list-2 validity
- Achievement test – Content validity
- Personality test – Construct validity
- Performance test – Concurrent validity
- Aptitude test – Predictive validity
- A researcher constructed a test in which items require students to answer some abstract concepts related to newton’s law of motion. Later, it was matched with the scores obtained in a class test for the same topic. It is a content type of validity that has been examined.
- A valid argument for conducting research in education
- For advancement of educational theory
- For improving educational practice
- For developing sound educational policies
- When there are two group of student to be compared for the performance of the groups – sign statistical test is used
- Wellness of the life style depends on the persons values and attitudes
- Research types in governemnt planning bodies descriptive studies.
- In a lab experiment controlling the variable is more important compared to other following acts
- manipulating the variables
- Arranging the lab conditions
- In a study the significance of difference between means was tested through use of a t test for a large group. The value of t being 2.10 decision warranted in respect of
- The h0 will be rejected at 0.05 level of significance level
- In the enquiry of experimental research, research design functions as a specific and precise guidance.
- For Attitude as variable in a research will provide ordinal measure
- Questionnaire for 5 different states is the appropriate research tool to find about the success about RTI iplmentation.
- Rubric is a set of criteria used for assessment
- correct for mixed methods research
- It provides in-depth understanding of a problem
- It combines experimental research with narrative research
- It integrates ‘numbers’ and ‘stories’.
- It involves qualitative and quantitative data as two distinct types.
- measurement scales from ‘the most precise’ to ‘the least precise’ method of quantification
- Ratio scale
- Interval scale
- Ordinal scale
- Nominal scale
- Triangulation in research essentially refers to a qualitative cross-validation.
- Any reliability coefficient practically remains in the range 0 to 1
- A correct sequence in a research study
- formulation of purpose statement, objectives and hypothesis
- ‘F’ value for a difference between boys and girls in achievement is 16 what will be its ‘t’ value 4.
- The research tools tendency to give socially desirable response is a potential obstacle to sound research
- Interview
- A most objective tool for assessing reflective teaching
- Video recording
- When findings of a given study are generalized for a population, it involves both Type-I and Type-II error.
- Within groups variance of F-ratio refers to Sampling error.
- Classroom interactions can be appropriately assessed by Observation schedule among others like Questionnaire, Interview, Test.
- Regarding a research hypothesis
- is more specific than a problem statement.
- is supported or not supported by theory.
- relates variables that can be measured, manipulated or categorized.
- In a study the significance of difference between means was tested through use of a ‘t’ test for a large group. The value of ‘t’ being 2.10, what will be the decision warranted in respect of
- The H0 will be rejected at 0.05 level of significance only.
- The association among variables in a scientific study is indicated quantitatively as
- Coefficient
- A test consisting of 40 items was administered to a group of students. The mean and standard deviation of the obtained scores were found to be 24 and 5 respectively. The reliability coefficient of the test equals 0·63
- An investigator intends to establish the relationship between educational status of mothers and academic achievement of students for coastal areas. Which of the following methods will be helpful in terms of research design – Ex Post Facto method.
- In a study the effect of peer learning is being studied in relation to students’ achievement and motivation. What type of research label will be acceptable for this study – Applied research.
- Set – I Set – II (Tools/Techniques) (Characteristics)
- Interview – Flexible tool enabling multi sensory channels to be used.
- Discourse analysis – Explores the organization of ordinary talk, explanations or social actions to fit a pattern.
- Questionnaire – Useful instrument for collecting survey information.
- Observation – Offers the researcher an opportunity to gather data from natural settings.
- The technique can not specify the probability of each unit to be included in the sample
- Quota sampling
- A researcher wants to conduct a large scale survey regarding the effectiveness of mid-day-meal scheme. For this purpose which tool will be suitable
- Questionnaire.
- If the correlation between the split-halves of a test is 0.68, using appropriate prophecy formula, the reliability of the test will be 0.809.
- Positivism is synonym of the word empiricism.
- Ethno methodological study is a Sociological approach
- A researcher has given 10 minutes extra to answer a test on intelligence to a group of students. This would result in this type of error – Systematic measurement
- Identify the probability sampling method from the following.
- Systematic
- The most appropriate measure to find the correlation between gender and pass and fail in a test.
- Point-biserial correlation
- The correct sequence of the steps followed in the educational research ?
- Selection of the problem
- Formulation of hypothesis
- Methodology
- Data collection
- Analysis and interpretation of data
- Report of result
- Percentage area of the normal probability curve of 3 standard deviation unit below and above the mean is
- 99.7
- Assertion (A) :Skewness influences regression.
- Reason (R) :Kurtosis measures flatness of frequency curve.
- (A) is true but (R) is false
- Kurtosis is a statistical measure that defines how heavily the tails of a distribution differ from the tails of a normal distribution
- If the majority of students score high marks in a test, then their distribution would be
- Negatively skewed
- Which means the scores are distributed so the curve tends to be negatively skewed
- In a positively skewed distribution – Mean > Median
- Type – II error means,
- We accept the null hypothesis although a true difference exists
- No error condition – Rejecting null hypothesis as there is no significant difference.
- We accept the null hypothesis although a true difference exists
- On a test with mean of 110 and a standard deviation of 10, an individual with a score of 140 will have a z-score of 3
- 140-110/10 = 3
- This poses a threat of internal validity
- Interaction of selection and maturation
- Specific feature which differentiates all experimental research from other method of research is Manipulation of independent variable
- This is an example for true experimental design Solomon four group design
- Causal-comparative studies are classified under Descriptive research
- If the kurtosis of a distribution is greater than 0.263 the distribution is Lepto kurtic
- When a researcher considers the individuals who are readily available as sample, then this sampling method is Incidental.
- The characteristics of a good measuring tool
- Objective in measuring
- Reliable and valid
- Usable
- Which test is used to ascertain an individuals achievement status with respect a well defined specific behaviour objectives
- Criterion referenced test
- The main purpose of establishing norms in a standardized test is
- Minimizing the interpretative error
- Subjectivity is least in this test
- Objective type
- When two genuinely dichotomous variables vary together in the same or opposite directions, the appropriate measure for indicating relationship is
- Phi coefficient of correlation
- A researcher working in the area of human intelligence wanted to develop a new verbal test of intelligence.
- He administered 2 variables by setting MCQ’s for two groups – Low Scoring and High Scoring.
- Phi coefficient of correlation
- An investigator wants to study the effect of gender on attitude towards Internal Evaluation by using two groups of students. The nature of this study would be
- Causal comparative
- A researcher has tested his/her research hypothesis through setting up a null hypothesis that, “…….. there is not significant difference between the two sets of data”. He/She finds that in the phase of available evidence,the H0 is to be rejected at the alpha level of 0.01. In that case, what will happen to his/her research hypothesis ?
- Research hypothesis will have to be accepted.
- In a research study, the problem formulated was as follows :
- Mother’s educational and professional status in relation to achievement motives of high school students belonging to coastal and non-coastal areas as influencing the learning outcomes in the subjects of social science and languages in the State of Tamil Nadu. Identify and label the following four variables of research in this problem and select appropriate code
- Label of the variable Variable indicated in the problem
- Independent variable – Mother’s educational and professional status
- Dependent variable – Learning outcomes
- Moderator variable – Achievement motives of high school students
- Control variable – State of Tamil Nadu
- In labelling research variables, the designations of variables from one research to the other have to be Different
- An aptitude test should essentially possess Predictive validity
- Assertion (A) : Mean is the most frequently reported measure of central tendency.
- Reason (R) : The computation of mean is based on each individual score of the sample.
- Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- For a sample of 225 cases, mean and SD are respectively 40 and 8. The 95% confidence interval in integral numbers, for true mean of the population is
- From 39 to 41
- A teacher undertakes a research project on developing a positive attitude towards school in order to assess the characteristics related to attitudinal behaviour. What research tool/technique will be most appropriate to use
- Questionnaire
- A researcher wants to explore whether a specific intervention program brings down absenteeism to a lower level. The research question is an example of
- Action research
- The combinations of approach that can be considered as important in action research design,
- Critical analysis of the situation
- Participatory approach
- Reflection
- The combinations of approach that can be considered as important in action research design,
- Action research
- A researcher is studying the effect of reinforcement on students’ achievement with appropriate controls imposed in practical situation. What is the type of research in this situation
- Applied research
- Further, supposing the researcher computes a value of ‘t’ for testing the significance of the difference between mean achievement of the two groups and finds that it is statistically significant. What decision would be warranted on the basis of this evidence
- The researcher rejects The Null hypothesis and retains the research hypothesis
- In order to lay down a procedure for testing the significance of ‘t’, the researcher has to decide in advance the alpha-level.
- T – score transformation corresponding to a Z – score of −1.5 will be 35
- Set – I Set – II
- Speed test(Reliability) – Kuder Richardson formula
- Internal consistency – Scores correlate with an established test
- Concurrent validity – Analysis of the meaning of test scores for the purpose it was constructed
- Predictive validity – Students are not allowed unlimited time to respond to all questions.
- When the subject and the respondent are one and the same person then the tool is called
- An Attitude Scale
- The mean and standard deviation of a set of scores are 50 and 10 respectively. If each raw score is increased by 3, the new mean and standard deviation would be (53, 10)
- List – I(Techniques of sampling) List – II (Characteristics of procedure)
- Purposive sampling – Researcher relies on his or her own judgment when choosing members from the population
- Multistage sampling – Dividing the population into subgroups and taking one or more groups at random
- Systematic sampling – Obtaining K ‘interval’ through N/n and using it for constituting the sample
- Stratified sampling – Researcher divides the entire population into homogeneous subgroups and randomly selects the final sample
- For computation of ‘F’ value in one way Anova, what is the final procedural step ?
- Finding out the ratio of between and within variance
- ANOVA for 4 groups of students tested in a research project Finding out the ratio of within and between sum of squares.
- If the computed values are used only to explain the properties of a particular sample taken for the study, the statistics used is called Descriptive statistics.
- The probability of committing type I error is tenable when a researcher Rejects H0 when it is actually true.
- A teacher is studying the impact of his personal association with students on students’ discipline in his/her class. This type of research may be called
- action and applied research
- The process by which indicators of a variable are made observable and measurable is called
- operationalizing the variable
- Assertion (A) :For controlling extraneous variables in an experimental design, random assignment of subjects is better than matching.
- Reason (R) : Matching tends to reduce the sample size.
- (A) is correct, but (R) is not a correct explanation for (A).
- Difficulty value of a question of an achievement test is indicated usually by computing : Percentage of students who answered that question correctly
- So, the normal distribution curve is negatively skewed since the percentage of students answered such question is high as it is easy.
- A test conducted by a classroom teacher for the purpose of identifying the strengths and weaknesses of students in a specified content area is technically called Diagnostic Test
- For collecting data in respect of attitude of school teachers towards the new curriculum, which of the following scales, will use summated rating scores as an indicator
- Likert scale
- The following example is of a hypothesis in a study undertaken at school level “School children from rural background are prone to less stress as compared to their counterpart in the urban areas”. This statement may be considered as an instance of which type of hypothesis ?
- Principal research hypothesis
- In arriving at generalizations in respect of findings, a researcher moves from
- Sample observations to population.
- As the main purpose remains Experimentation with controls and manipulation of variables.
- In which tool of research the coverage of information is relatively large and indepth
- Observation
- the following may not be considered as a source of hypothesis formulation
- Related studies surveyed by the researcher.
- A set of scores has a mean of 20 and a standard deviation 6. If every score is multiplied by 4, the new mean and standard deviation would be
- 80, 24
- F-test is used when more than two dependent or independent groups are to be compared
- The Phi-Coefficient is related to tetrachoric ‘γ’ in the same manner as biserial is related to Point biserial (γ)
- A researcher finds out the relationship between three variables such as academic achievement, intelligence and socio-economic status of children using Pearson’s product moment ‘γ’. As per objective of his/her study the relationship between academic achievement and intelligence is also to be estimated by controlling the influence of socioeconomic status. Which statistical technique will be appropriate in this context – Finding out partial correlation
- A researcher finding out the relationship between three variables use statistically appropriate technique to find out the partial correlation.
- To know the influence of extraneous factor on 2 independent variables.
- A researcher finding out the relationship between three variables use statistically appropriate technique to find out the partial correlation.
- Contributors related to Logical Positivism
- A.J. Ayer
- Bertrand Russell
- Rudolf Carnap
- A researcher has tested his/her research hypothesis through setting up a null hypothesis that, “…….. there is not significant difference between the two sets of data”. He/She finds that in the phase of available evidence,the H0 is to be rejected at the alpha level of 0.01. In that case, what will happen to his/her research hypothesis
- Research hypothesis will have to be accepted.
- In the process of standardization of a multiple choice test, the researcher while doing item analysis wants to test the hypothesis for each item response. The most appropriate statistics the researcher may use will be
- chi square test
- The association among variables in a scientific study is indicated quantitatively as Coefficient.
- The variance that reflects the systematic differences between groups in a research situation is termed as Experimental variance.
- An investigator studied the relationship between choice of stream (Art, Science, Commerce) and the development of reasoning ability. This study may be classified as Ex-post facto study
- List I (Method of Correlation) List II (Conditions for use)
- Point Biserial – One variable genuinely dichotomous, one variable continuous
- Product moment – Both the variables are continuous or interval measures
- Tetrachoric – Both the variables are artificially dichotomized
- Spearman’s rank – Both are ordinal measures
- In a research undertaken by a school teacher in respect of critical understanding of the students of his/her school, the following results were obtained :Mean=50 σ=10 N=100 Indicate the range of scores at alpha level 0.05 for finding the value of true mean for the population of such students in the whole district.
- From 48.04 to 51.96
- t value for 0.05 = 1.96
- 1.96 * 10/root 100 = 1.96
- Confidence interval = 50+- 1.96
- From 48.04 to 51.96
- A systematic, objective and deliberate effort at answering meaningful questions pertaining to a field of enquiry or about phenomena is called Research.
- A student wants to know whether he will perform well in a particular job. Which of the following tools will predict this Aptitude test
- The term population in research is defined as the total number of cases in a group.
- In which tool of research the coverage of information is relatively large and indepth
- Observation
- The scientific theory as developed by Taylor in respect of administration can be described by a set of statements like the ones given below. Identify the correct set from the codes given
- A rule of thumb should be replaced by the organized knowledge.
- The administrator should follow his/her discretion in running the organization.
- Instead of individualism, cooperation should be the focus.
- In a study on tribal community the researcher finds that there are several groups in which the members exist. As an advise to the researcher for the choice of sample which method from among the following you will recommend – Cluster sampling
- The measurement of an entire population yields
- Parameter
- As a researcher you want to evaluate the teaching performance of a teacher. Which of the following tools will be most appropriate
- Rating scale
- Internal criticism of data is considered important in which of the following research
- Philosophical
- It is related to Ex Post Facto research
- Random assignment of subjects to the treatment group is not possible
- Dependent variable is measured first and independent variables are studied after that.
- Provide support to any number of different and sometimes contradictory hypotheses
- It is not possible to exercise control in the study.
- The methodology section in a quantitative research paradigm-based article contains Participants, instruments, procedures.
- a sequence of logical steps using quantitative paradigm in the formation of research problems are
- Determining the field of study.
- Deciding the specific problem.
- Identifying the variables involved
- Defining and delimiting the scope of the problem
- Evaluating on the basis of personal and academic suitability of the problem.
- a sequence of logical steps using quantitative paradigm in the formation of research problems are
- Standardized tests are different from locally devised tests in that, they have norms, uniform administration and scoring.
- the following research tool / technique will be appropriate for an indepth understanding of cultural and social aspects of a tribe
- Participant observation
- In experimental studies, the effect of a variable which cannot be observed but can only be inferred, is termed as Intervening variable.
- A researcher asked questions to several individuals systematically and simultaneously by bringing them together in a comfortable environment in a guided discussion. Which of the following techniques did he use ? Focus group technique
- A: Focus group involves structured interview
- R: It involves interaction among participants moderated by the researcher as a source of data
- The coverage of information is relatively large and in-depth in this research tool.
- A: Focus group involves structured interview
- A researcher wants to explore whether a specific intervention program brings down absenteeism to a lower level. The research question is an example of Action research
- a small scale intervention in the functioning of the real world with an intent of a close examination of the effects of such intervention.
An investigator intends to establish the relationship between educational status of mothers and academic achievement of students for coastal areas. Which of the following methods will be helpful in terms of research design Ex Post Facto method
a valid argument for conducting research in education For advancement of educational theory, For improvement of educational practices, For developing sound educational policies.
In a study the effect of peer learning is being studied in relation to students’ achievement and motivation. What type of research label will be acceptable for this study? Applied research
For conducting a study to understand the social customs in a tribal society, which of the following technique will be most appropriate Participant observation.
In order to ensure that the impact on dependent variable is only due to independent variable, which of the following methods will be more appropriate Experimental method.
| List – I | List – II |
| (Type of research) | (Description) |
| (a) Naturalistic inquiry | (i) prefer inductive reasoning from grass rootsobservation and discovery with an emergent design |
| (b) Phenomenological research | (ii) analysis of qualitative data to provide anunderstanding of a concept from the participant’sperspective |
| (c) Ethnographic research | (iii) analytical description of social group related to theshared beliefs, practices and behaviours. |
| (d) Grounded theory research | (iv) sophisticated analysis which links participantperception |
- In a study conducted on two matched groups, the researcher attempts to find out the effect of teacher controlled and learner controlled instruction on the achievement of rural and urban students of higher secondary level, what is the independent variable in this study? Teacher – controlled Vs. learner controlled instruction.
- Identify the statement showing the positive strength of internet as a resource for literature review Research posted on websites is typically current information
- Section – I Section – II (Method of Sampling) (Purpose Served)
- Multi stage sampling – Selecting the sample in stages.
- Quota sampling – Give proportional weight-age to selected characteristics of the wider population
- Snow ball sampling – Sampling a population where access is difficult and the selected individuals are then used as informants.
- Purposive sampling (iv) Purpose of sampling changes at each stage of the procedure so that to hand pick the cases on the basis of their typical characteristics.
- Dimensional sampling – Identifying various factors of interest in a population and obtaining at least one respondent of every combination.
- If an individual obtained a Z-score of 0.5 in a test, the corresponding T-score would be 0.55
- Quota sampling technique can not specify the probability of each unit to be included in the sample.
- In a case study of truant children in a school a few cases have to be identified to compose the sample. Which of the following sampling procedures will you recommend for the sample of the case study – Snow ball sampling
- The following forms part of qualitative research where research design sampling is least necessary
- Case study, Participant observation, Naturalistic enquiry
- The standard deviation of sampling distribution of a statistic is known as Standard Error.
- Standard error is an index of Errors due to sampling.

Recent Comments