Meaning and Scope of Educational Research:–
- The correct sequence of actions in conducting an intervention-based action research in education,
- Plan, act, observe and reflect
- Selection of the problem
- Formulation of hypothesis
- Methodology
- Data collection
- Analysis and interpretation of data
- Report of result
- Plan, act, observe and reflect
- The distinctive feature of case study research
- Developing an in-depth understanding of the case.
- In case study based research method, generalizations is made that will be applicable to other situations of the same type.
- This research method lays emphasis on naturalistic settings and meaning-giving processes.
- From the list given below, identify the statements which appropriately describe the main characteristics of steps in a scientific method
- Identifying and defining the problem
- Formulating hypothesis
- Collecting, organizing and analyzing data
- Formulating conclusions
- Verification, rejection or modification of the hypothesis.
- A school teacher plans a research study to find out the relationship between level of aspiration and socio-economic status of students’ parents. Which type of research design will be appropriate for this study – Non-experimental research design.
- To study the relationship between variables which cannot be manipulated by the researcher– Non-experimental
- Eg. A university teacher intends to study the relationship between the level of aspiration and achievement of rural children.
- In this study, the variable achievement depends on the natural setting of the child that decides the level of aspiration.
- An investigator wants to study the functioning of a school meant for tribal children. The most appropriate research design for this context would be classified as
- Ethnography
- A type of research method that probes with an eye on interpreting their patterns of adjustments
- The researcher in ethnographic research gets immersed in social selfing for an extended period of time by listening and engaging in conversation.
- In ethnographic probing, Research method- an empiricism inductive paradigm is employed ethnographic probe.
- In ethnographic research, a researcher uses a non-interactive strategy, which describes people’s shared experiences and connotes their feelings.
- It is known as Artifact collection.
- Ethnography
- The main purpose of research is to formulate generalizations leading to theory building – experimentation with controls and manipulation of variables.
- Three types of investigation in ascending order in terms of the researcher’s ability (usually) to control secondary variance
- Ex post facto field studies
- Field experiments
- Laboratory experiments
- The main difference between Laboratory Experiment and Field Experiment’s is :
- Degree of control of extraneous variables.
- The following research designs is the most appropriate for depicting lived experiential realities – Phenomenological designs.
- Analysis of qualitative data to provide an understanding of a concept from the participant’s perspective
- It is one of the post positivist approach which involves the participants perspectives.
- So, no hypothesis testing is done in this type of research.
- The following statements are true for a historical research design,
- Mostly based on qualitative data.
- Data are examined for validity and authenticity.
- Content-analysis is used for data treatment.
- Historical evidence becomes the basis of writing the report in historical research
- Emphasis of historical research lays on collecting and collating data from the past.
- Content analysis is used for data treatment for validity and authenticity.
- Investigator conducted a study to examine the effect of gender on attitude towards dowry system. The nature of this study was Causal comparative.
- It neither controls extraneous variables, nor does it manipulate independent variables – So experiment cannot be conducted in such a study.
- List I (Types of Research) List II (Description)
- True experimental research – Cause-effect relationship between manipulated conditions and measured outcome.
- Basic research – Concerned with theory building and explaining natural phenomena.
- Applied research – Exploring the possibility of use of theory in varied situations. (The effect of peer learning is studied in relation with achievement and motivation).
- Evaluation research – Judging the worth of a particular practice.
- An example of a distal method in Educational Psychology is ex-post facto method
- Dependent variable is measured first and independent variables are studied after that.
- Since it probes into the causal factors from the observed effects.
- So, Random assignment of subjects to the treatment group is not possible.
- For instance, a university teacher intends to study the relationship between the level of aspiration and achievement of rural children.
- The formulation of generalization get more attention in Ex-post facto studies.
Qualitative Research Designs:
- In which of the following modes of testing, a student is given optimum scope for displaying his/ her accomplishment?
- Power test.
- The student gets enough time to show what he/she knows.
- Power test.
- Discourse analysis method of the qualitative research focuses on language and meanings that are given to texts, for the purpose of creating and shaping knowledge and behaviour.
- It explores the organization of ordinary talk, explanations or social actions to fit a pattern.
- The combination of different approaches to validate information,strategies, and results in a research study is technically known as :
- Triangulation
- It is a method which involves the use of two or more than two research tools.
- A process of data collection strategies that cross-validates information across different data sources.
- In research it essentially refers to a qualitative cross-validation.
- Triangulation
- Which of the following research designs utilizes data from individuals, autobiographies and personal talks/discussions?
- Narrative research design
- The characteristic of this qualitative research paradigm involves,
- Collecting individual stories.
- Collaborating with participants
- Chronology of the experience.
- Narrative research design
- Mixed methods research does not involves qualitative and quantitative data as two distinct types.
- It provides in-depth understanding of a problem
- It combines experimental research with narrative research
- It integrates ‘numbers’ and ‘stories’.
- The following represents the distinctive feature of qualitative research
- Perspective based, inductive and meaning giving.
Techniques of sampling:
- Section – I(Method of Sampling) Section – II (Purpose Served)
- Multi stage sampling – Dividing the population into subgroups and taking one or more groups at random
- Quota sampling – Give proportional weightage to selected characteristics of the wider population
- Stratified sampling – Researcher divides the entire population into homogeneous subgroups and randomly selects the final sample.
- Snow ball sampling – Sampling a population where access is difficult and the selected individuals are then used as informants
- Purposive sampling – Purpose of sampling changes at each stage of the procedure.
- In the process of drawing a random sampling which of the following process is in order of sequence?
- Define target population, decide sample size, list all the units of target population and drawing the sample by randomization.
- These are probability sampling procedures eg. simple random, stratified random, cluster.
- In case the population of the research which is heterogeneous in nature, stratified random sampling techniques will ensure optimum Representative of sample units.
- To reduce random error – Administer the treatment, in the same way, every time.
- Define target population, decide sample size, list all the units of target population and drawing the sample by randomization.
- The essential element that differentiates between ‘probability’ and ‘non – probability’ sampling technique is
- Randomness in the selection of units
- For controlling extraneous variables in an experimental design, random assignment of subjects is better than matching.
- Randomness in the selection of units
- A method of sampling that ensures proportional representation of all sections of a population is technically called Stratified Sampling.
- A: Randomization is the best method of controlling the effect of extraneous variables in research.
- (R) :It results in the equal spread of effect of most of the extraneous variables.
- Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
- The element that differentiates between stratified and quota sampling techniques is Randomness in the drawing of units.
- A researcher intends to study the adjustment problems of students who are slum dwellers. What should be the sampling procedure used for such a study?
- Cluster sampling
- Cluster sampling method – Selects a specific group of individuals from a widely dispersed population.
- In a study on tribal community the researcher finds that there are several groups in which the members exist.
- As an advise to the researcher for the choice of sample cluster sampling method is recommended.
- The probability of each unit included in the sample by stratified, systematic and cluster sampling during the randomness in the selection of units.
- Cluster sampling
- Match the items in List-I (Techniques of sampling) with that of List-II (characteristics of procedure)
- Purposive sampling – Researcher relies on his or her own judgment when choosing members from the population – Seeks cases according to his/her judgement about the appropriateness
- Multistage sampling – Dividing the population into subgroups and taking one or more groups at random
- Systematic sampling – Obtaining K interval through N/n and using it for constituting the sample
- Stratified sampling – Researcher divides the entire population into homogeneous subgroups and randomly selects the final sample
- Set-I (Approaches to sampling in qualitative research) and their characteristics in Set-II (Characteristics)
- Extreme case sampling – Seeks cases that are unusual
- Purposive sampling – Seeks cases according to his/her judgement about the appropriateness
- Snowball sampling – Seeks help from participants to identify additional participants
- The following are non-probability research methods,
- phenomenology based researches
- action researches
- It utilises Non-Probability Sampling’ procedures with empirical inductive research paradigm
- Dimensional sampling
- Snowball sampling
- Quota sampling
- Dimensional Sampling – Identifying various factors of interest in a population and obtaining at least one respondent of every combination.
- In a case study of truant children in a school a few cases have to be identified to compose the sample.
- Snow ball sampling of the case study is recommended to obtain the network of factors related to such case.
Types of Measurement Scale:
- List I (Types of variable) List II (Correlation coefficient) Conditions for the method of correlation
- Both variables continuous or interval measures – Pearson’s product ‘r’ –
- Both are ordinal measures – Spearman’s rank artificial dichotomy
- artificial dichotomy – Tetrachoric r – Both the variables are artificially dichotomized
- One variable genuinely dichotomous, one variable continuous – Point Biserial
- Two or more categories – Contingency coefficient
- The correct order of measurement scales in increasing order of accuracy, precision and number of operations used
- Nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio.
- A teacher prepares a list of latest arrivals in the various libraries of the colleges of a university.
- His list reflects the number of books as reported. Ratio method of the measurement scales is implied.
- Set – I (Types of Measurement scale) Set – II (Application)
- Nominal Scale – Listing students according to participation in Co-curricular activities – Checklist
- Ordinal Scale – Superior performance in musical events – Rating scale
- Interval Scale -Performance scores on a spelling test – Numerical scale
- Ratio Scale – Speed of students in writing words per minute.
- Research tools and Measurement scale and Properties
- Nominal scale of measurement – classification – Questionnaire and interview.
- an ordinal scale of measurement -classification and order – Attitude and value test – causal comparative, ethnographic and case studies – Percentile score
- Interval scale of measurement – classification, order and equal units – intelligent and aptitude test
- ratio scale of measurement – classification, order, equal units and absolute zero – speed and frequency test.
- While assessing the attitude of administrators towards women empowerment programme a researcher had no preconceived notions about what she might discover, and she continued interviewing until key themes emerge. This paradigm of research Grounded theory approach
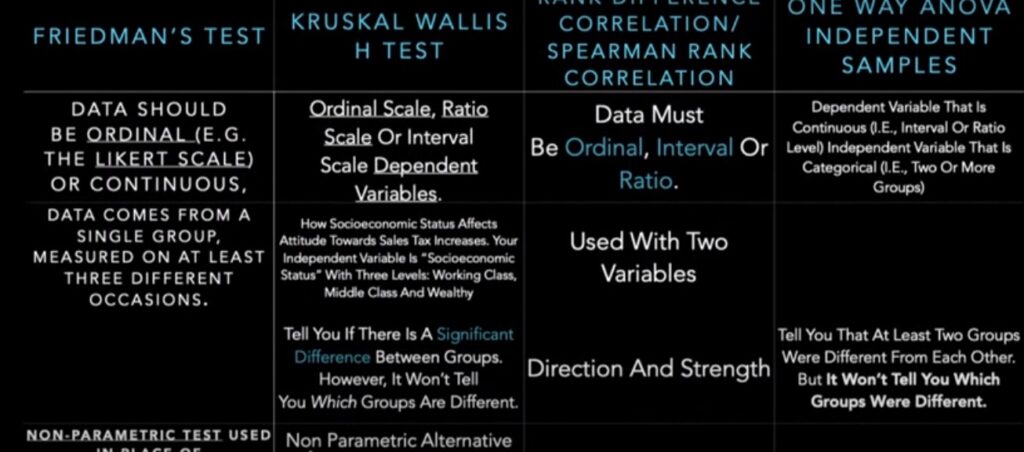
- The statistical technique will be appropriate for data analysis when the observations are available in the form of frequencies
- Non-parametric ‘chi-square’ test
- parametric test
- Analysis of Variance
- Median Test
- Critical Ratio
- Independent t-test
- A group of 10 students was randomly drawn from Class 12 and was given yoga training for three weeks. Their wellness life style was compared with another similarly selected group which did not undergo such training. Which type of statistical test will be appropriate for testing the tenability of Null Hypothesis ?
- Independent t-test
Statistical techniques :-
- Quantitative research is also called the Structured approach
- At the stage of data analysis in which quantitative techniques have been used by a researcher. The evidence warrants the rejection of the Null hypothesis(Ho). The decision of the researcher which is deemed to be appropriate –
- Rejecting the null hypothesis(Ho) and accepting the substantive research hypothesis.
- Which of the following are the assumptions underlying the use of parametric statistics:
- The variable being studied is continuous (Interval based measurements)
- Scores are normally distributed
- Variances over all groups are equal
- For use of a non-parametric test like the chi-square, No assumption about the nature of distribution is required.
- Chi-square test is a distribution free test.
- Conditions which holds good for non-parametric test
- no assumption about the defining properties of population.
- Methods that do not use distributional assumptions.
- Use of data that obtained as interval or ratio measure.
- Generalization of attitude based on the interdependence of variables like motivation and performance.
- Meta analysis is a review process which uses statistical techniques to synthesize the results of independently conducted prior studies.
Correlation coefficient:
- Set-I (Type of correlation) Set-II (Conditions)
- Biserial correlation – One variable is continuous and the other is artificially dichotomous
- Point biserial correlation – One variable is a genuine dichotomy and the other is an interval measure (Continuous).
- Tetrachoric correlation or Rank order correlation – Both the variables are in a forced dichotomy or an ordinal scale
- Phi coefficient of correlation or Product moment correlation – Both the variables are genuinely dichotomous with an interval scale.
- A psycho-metrician wanted to develop a new test of abstract thinking. So prepared a test of 80 items with each having 5 alternate answers.
- To obtain inter-item correlation coefficient phi-coefficient is used in the analysis.
- Since there are two genuinely dichotomous variables which vary together.
- Correlation coefficients that can be considered as non-parametric in nature Rank difference correlation.
- While parametric tests that controls the effect of one or more variable is partial correlation.
- An educational researcher wants to study the relationship between academic performance and motivation by keeping the effect of a third variable such as socio – economic status neutral. Which of the following technique of correlation will be appropriate in such a situation – Partial correlation
- A simple correlation was calculated between two variables after removing the effect of a third variable from both, the resulting correlation – Partial correlation
- A researcher finds out the relationship between three variables such as academic achievement, intelligence and socio-economic status of children using Pearson’s product moment ‘γ’. As per objective of his/her study the relationship between academic achievement and intelligence is also to be estimated by controlling the influence of socioeconomic status. Which statistical technique will be appropriate in this context – Finding out partial correlation.
- Both variables continuous – Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
- In a study, a researcher wants to eliminate the effect of one variable in a bid to find out the pure relationship between two variables of his/her interest. He/She should be advised to use which of the following methods of computing coefficient of correlation – Partial correlation.
A simple correlation was calculated between two variables after removing the effect of a third variable from both, the resulting correlation is called Partial correlation
Data Analysis:
- A researcher uses both t-test and F-test on the same data obtained from two groups. The
functional relationship between values of t and F if calculated would be t^2= F.- T – score transformation corresponding to a Z – score of −1.5 will be 35.
Measures of Central tendency:
| z value | T-value |
| 2 | 70 |
| 1.5 | 35 |
| 0.5 | 0.55 |
- A group of 10 students was randomly drawn from Class 12 and was given yoga training for three weeks. Their wellness life style was compared with another similarly selected group which did not undergo such training. Which type of statistical test will be appropriate for testing the tenability of Null Hypothesis ?
- Independent t-test
- Given a Mean = 100 ; S.D. = 20 ; and N = 100. Which one of the following will be the correct statement for indicating the possibility of population mean at 0.01 level of confidence ? Population mean falls between 94.8 to 105.2
- degree of freedom = 100-1 =99
- value of t = 2.62
- E = 2.62*20/Root 100
- =2.62*20/10 = 5.24
- Confidence interval = 100+-5.24 = 94.8 to 105.2
- A college librarian plans the purchase of books keeping in view the demand of different books among students. Which of the following measures of central tendency would be suitable for this purpose? Mode.
- In a normal distribution, three measures of central tendency coincide.
- Which of the following measures is used for describing the units of differences from the central tendency measure such as mean ? Standard deviation
Testing of Hypothesis:
- True in the case of good hypothesis:
- It is derived from the existing theory of knowledge.
- It indicates the relation between variables postulated.
- It is stated in a concise and lucid manner.
- A research hypothesis,
- It is more specific than a problem statement.
- It is supported or not supported by theory.
- It relates variables that can be measured, manipulated or categorized.
- In randomly constitute two groups experimental and control, a researcher obtains the following results after using a parametric ‘t’ test. Value of t = 3 for N = 300.
- On the basic of this evidence which decision in respect of substantive research hypothesis and the null hypothesis will be justified
- Rejecting the null hypothesis and accepting the research hypothesis
- At the data analysis stage, whenever the evidence warrants the rejection of the Null hypothesis(Ho) the decision of the researcher is to accept the substantive research hypothesis.
- Parametric ‘T’ test is conducted to establish correlation between two variables in the form of nominal data.
- On the basic of this evidence which decision in respect of substantive research hypothesis and the null hypothesis will be justified
- Given a Mean = 100 ; S.D. = 20 ; and N = 100. Which one of the following will be the correct statement for indicating the possibility of population mean at 0.01 level of confidence Population mean falls between 94.8 to 105.2
- In a research study the variable which is not directly observable but whose effect is inferred on the dependent variable is termed as Intervening variable.
- In Hull’s system of learning Sampling error reaction potential was postulated as an important intervening variable.
- Need-reduction theory of learning
- Hierarchy of needs
- Stimulation and drive
- Habit strength or intensity of stimulus
- Stimuli
- Effective reaction or Number of non reinforced responses for extinction
- In Hull’s system of learning Sampling error reaction potential was postulated as an important intervening variable.
- An investigator used T-test to compare two groups of students on verbal aptitude.
- He repeated his experiment 20 times and obtained significant difference 19 times. On the basis of this he decided to reject the null hypothesis. The probability of committing type I error was 0.05.
Sampling Error:
- A researcher used t-test to compare two means based on independent samples and found the t-value to be significant at .05 level. This means that chances are 5 out of 100 that the difference between means has occurred due to sampling errors.
- An investigator used t-test to compare two groups of students on verbal aptitude. He repeated his experiment 20 times and obtained significant difference 19 times. On the basis of this he decided to reject the null hypothesis. The probability of committing type I error was 0.05
- A researcher has tested his/her research hypothesis through setting up a null hypothesis that, “…….. there is not significant difference between the two sets of data”. He/She finds that in the phase of available evidence,the H0 is to be rejected at the alpha level of 0.01. In that case, what will happen to his/her research hypothesis – Research hypothesis will have to be accepted.
- A: The research hypothesis being the alternative hypothesis (H1 ) has to be kept in the domain of acceptability.
- The Null hypothesis (H0) has been rejected at high alpha (significance) level thereby rendering the possibility of Type I error quite insubstantial.
- Statement I: As the alpha level becomes more stringent — goes from 0.04 to 0.01 the power of a statistical test decreases
- Statement II: A directional hypothesis leads to more power than a non — directional hypothesis
- Both Statement I and Statement II are true
- As the power of a statistical test decreases gives rise to Type 2 error, though null hypothesis is false it is accepted.
- On the contrary, on raising the level of significance increases the possibility of committing type I error.
- Type 1 error is rejecting a true null hypothesis.
- Thereby, At Higher level of significance increases the probability of rejecting the true hypothesis
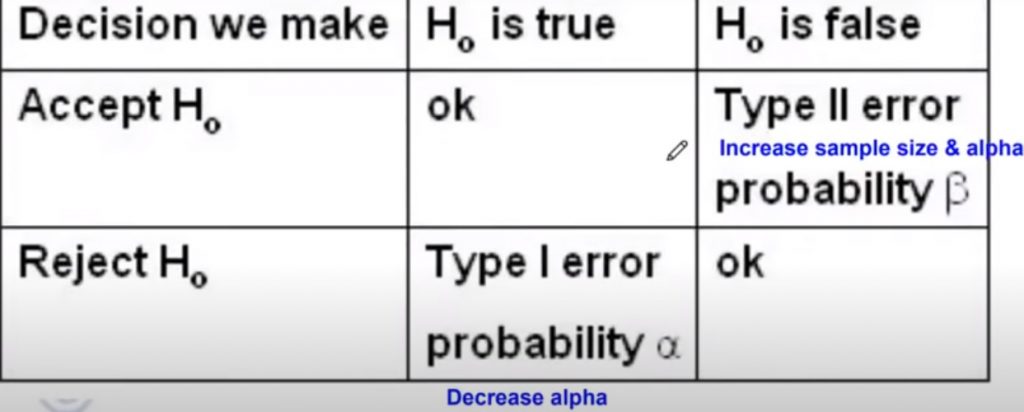
- Type-I error, in the testing of a null hypothesis, occurs when the researcher rejects it when it is true
- In the process of statistical inference, the Type II error is committed when we Reject a true null hypothesis, although a true difference exists.
- A researcher commits Type I Error when he rejects the Null Hypothesis when it is true.
- An investigator commits type II error when he/she accepts a null hypothesis when it is false.
- When there is no significant difference usually rejects null hypothesis.
- Type II error = accepting the null hypothesis as there is a true difference.
- In a study regarding two types of video games and their relation to play way method of teaching, four types of conclusions can be arrived at, as listed below.Identify which of the statements can be treated as
- Type II error – Deciding the two types of video games are not related to play way method of teaching and they really are.
- In rejecting a null hypothesis (H0 ), a researcher is likely to commit which type of error – Type I error.
- A weighing machine mostly over measures the weight of individuals. It will be said to be indicative of
- Systematic Error.
- The difference between a sample statistic and the corresponding parameter is known as sampling error.
- Standard deviation of a sampling distribution of a statistic is termed as Standard error.
- Within groups variance of F-ratio refers to Sampling error
- The square root of Variance is Standard Deviation.
- On obtaining representative sample, there is a tendency to decrease sampling error.
- When the standard error of measurement is small – a test-user have more confidence in the precision of test scores
- Standard deviation of a sampling distribution of a statistic is termed as Standard error.
- In a study the significance of difference between means was tested through use of a ‘t’ test for a large group. The value of ‘t’ being 2.10, what will be the decision warranted in respect of H 0 (Null hypothesis) ?
- The H 0(null) will be rejected at 0.05 level of significance only.
- Higher level of significance increases the probability of rejecting the true hypothesis
- Raising the level of significance increases the possibility of commiting type I error.
- The H 0(null) will be rejected at 0.05 level of significance only.
Tools of Research:
Reliability:
- Which of the following statement are true from reliability of a research tool?
- It is correlation of scores on the testing tool itself.
- It varies from sample to sample.
- It is affected by the size of the sample.
- It is affected by variance of scores as it is not fixed for a given test.
- In research, reliability is the quality of a measurement procedure which provides repeatability and accuracy.
- A common test in research demands much priority on Reliability, and Objectivity.
- achievement test,
- Intelligence test,
- aptitude test = Predictive validity
- In research, reliability is the quality of a measurement procedure which provides
- Repeatability and accuracy
- One way to measure the extent to which a measure is free of random error is to compute its test-retest reliability
- The correlation coefficient between scores on two parallel tests was found to be 0.48. If both the tests are combined, the reliability coefficient of the combined test would be 0.65.
- ANOVA tehnique is used for estimating the reliability of a measure – Intra-class correlation.
- Finding out the reliability, validity and norms is the penultimate step of the logical sequence of steps in standardization of tests
- then follows Developing test manual
- Standardised tests are deviced to have norms, uniform administration and scoring
- A good research tool is identified on the basis of reliability index coupled with its validity.
- Internal consistency estimates of reliability are widely used for the reasons when :
- the reliability coefficient is usually very high
- it is more dependable than stability and equivalence estimates
- only one form of the test is needed
- it is the easiest way to calculate reliability.
- Which of the following methods of reliability of a test describes the average correlation of all split half correlations and can be applied when there are more than two options to each item ?
- Cronbach’s alpha.
- It’s a technique used for estimating reliabilty of multiple- trials tests.
- Split half method of reliability – Spearman-Brown formula.
- With split-half reliability, the two tests are given to one group of students who sit the test at the same time.
- However, the two sets do not have to be equivalent.
- A reliable test will have high correlation, indicating that a student would perform equally well (or as poorly) on both halves of the test.
- A measure of internal consistency that measures test components contribute to construct that is being measured.
- Cronbach’s alpha.
- List-1 (Types of reliability) and List-2 (Procedure)List-III : (Method of estimation)
- Equivalence and Stability – Administer different tests to the same individuals over a period of time.
- Equivalence – Administer different tests to the same individuals at about the same time – Parallel form method – Standard error of measurement for one form is the same as the other.
- Stability – Administer the same test to the same individuals over a period of time – Test -retest method
- Internal consistency – Administer one test and correlate the items to each other- Split – half method
- it is the easiest way to calculate reliability
- the reliability coefficient is usually very high and cannot be negative
- It is the correlation of the test with itself.
- it is more dependable than stability and equivalence estimates(Test and test )
- (Type of reliability coefficient) (Sources of error variance)
- Test – retest- Time sampling – a method to determine reliability
- Kuder – Richardson – Heterogeneity of test items
- Split – half – Homogeneity of test items
- Alternate form – Content sampling
validity:
- Not an ecological threat to external validity of experimental research : – Subject – treatment interaction
- External validity of any educational research refers to the extent the findings are generalized to populations.
- In case of large sample size. Generalization of research results into questionable
- A researcher conducts an experimental study by imposing several controls in respect of sample, data collection tools and situational variables.
- The likelihood of threat in arriving at generalization in this context will be to External validity.
- When results obtained in 6 research study can be extended to a group larger than the sample(outside the context of the study) it is called – External validity – Treatment and no-treatment groups were unequal before the study began
- an ecological threat to external validity of experimental research
- Multiple treatment interference
- Setting – treatment interaction
- Reactive arrangements.
- List I (Characteristic of Validity Measure) List II (Type of Validity)
- Measure of product or performance – predictive validity
- Measure of un-observable – Construct validity – Analysis of the meaning of test score in terms of a stipulated purpose.
- Measure of representation of substantive knowledge structure – Content validity
- Extent of agreement between two measures – concurrent validity.
- Assertion (A): Concurrent validity coefficients are generally higher than predictive validity coefficient
- Reason (R) : This does not mean that the test with higher validity coefficient is more suitable for a given purpose
- Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- An investigator conducted the factor analysis of tests to be used in research. It means, he was interested in Construct validity
- Internal Validity – Sample of participants was not representative.
- Subject – treatment interaction for selecting and maturation of samples.
- statistical indices of internal consistency can be calculated by
- Mean inter-item Correlation
- Cronbach’s Alpha
- statistical indices of internal consistency can be calculated by
- Internal evaluation – enhance the validity and dependability of the evaluation outcomes.
- Subject – treatment interaction for selecting and maturation of samples.
- Artifacts that arise and affect the internal validity in research are
- History – Extraneous variables occur during research and affect the results.
- Maturity – Effect due to natural changes in the subjects
- Instrumentation – Tests or responding to a questionnaire affects the subjects.
- Experimental Mortality – Systematic loss of subjects.
Case Study 1:

- If the project in-charge developed a 75 item version by adding similar items. The expected cronbach’s alpha (Measure of internal consistency or reliability)
- 25*3=75
- r n(new reliability) = r0(old reliabilityy) * k(Number of times) / 1+(k-1)*r0
- cronbach’s alpha = 0.7*3/1+(3-1)*0.7 = .87
- Which one of the following correlation is most suitable for computing item- remainder correlations?
- Point biserial correlation – Relation between dichotomous items and continuous of total items
- Number of question – continuous scale
- Answers are in dichotomous state – right or wrong
- Point biserial correlation – Relation between dichotomous items and continuous of total items
- Consider three reliability co-efficients:-
- Split-half reliability coefficient
- K- R reliability coefficient
- Cronbach-alpha. True to this context
- All 3 methods are internal consistency or reliability
- K-R 20 used for dichotomous variables
- Alpha used for continuous variables
- KR-20 and Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficients are same while Split half has different methodology.
- A: The computation of KR reliability is questionable in the above study
- R: K-R relaibility is suitable for tests with dichotomous items
- For K-R the response of item is dichotomous whether right or wrong ( 0 or 1), So it is not questionable but certain to employ KR method
- A is false but R is correct
- R: K-R relaibility is suitable for tests with dichotomous items
- The above information provides
- alpha =0.7(Note 0.7 and above satifactory)
- r(test-retest) = 0.26 (Note: low) with significance 0.01
- test – retest reliability is Unsatisfactory @ 0.26
- Acceptable internal consistency reliability of 0.7(Cronbach’s alpha)
- Note: Reliability and validity- strength of correlation so no need for significance level.
Case Study-2:

- Expected cronbach alpha for form – A will be
- When the no. of items are higher (homogenous items) reliability(Cronbach’s alpha) is higher
- 0.94, 0.89,0.62 and 0.47
- Since 110 items got reduced to 80 items
- Correlation would reduce from 0.94 to 0.87
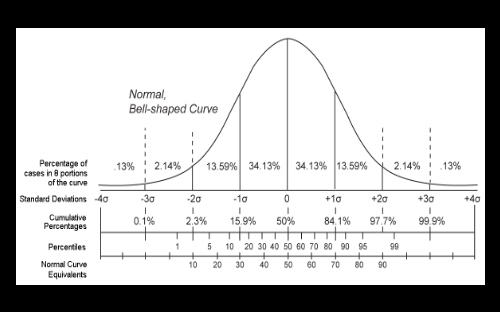
- 95% confidence interval for the true score of 32 would be
- 32+-1.96+1.96 (From mean 50, 32 is 2 S.D away)
- Z value of 95% in normal dbn= 1.96 so for 2 SD = 1.96*2=3.92 Note(For 99% = 2.58)
- 32+-3.84
- the score of 32 (by manas on 80 item version)would correspond to percentile rank
- 16,32,80,84
- (From mean 50, 32 is 2 S.D away)
- 50-34.13 = 15.9%
- 16,32,80,84
- Item remainder correlation
- Item-1 Response-1, 2, 3, 4 total correct –
- Chemistry 1 0 0 0 –
- Dichotomous – Response – correct or wrong response
- Continuous variable – chemistry test questions
- Point bi serial correlation
An experimenter administered a pretest on both experimental and control groups and found that the pre-test mean scores of the groups differ from the following statistical techniques can address this difference in studying the impacts of independent variable – Analysis of co-variance.
For estimating maximum value of multiple correlation of independent variable,
- Independent variables should correlate high with the dependent variable.
- While, the independent variables should correlate low with one another
A study was designed to estimate the effect of four different methods of providing feedback to elementary school level students on their spelling ability. At the level of data analysis which of the following statistical technique will be considered appropriate for hypothesis testing in this study – Fisher’s ‘F’ test. So, it’s used when more than two dependent or independent groups are to be compared
A school principal gave a spelling test to 256 students. The distribution of scores was found to be normal with a mean of 42 and standard deviation of 8 points. The probability is 0.95 that the mean of corresponding population would be less than the upper limit of 42.98
A group of 10 students was randomly drawn from Class 12 and was given yoga training for three weeks. Their wellness life style was compared with another similarly selected group which did not undergo such training. Which type of statistical test will be appropriate for testing the tenability of Null Hypothesis?Independent t-test.

Recent Comments