Meaning and Nature of planning:
- Planning is one of the formal duties of the management of an institution.
- Planning is always done in advance in such a way that all the things happen in a system and in a systematic way.
- Planning means leading before hand, how things are to be done and why it should be done in that way.
- In order to make the school activities effective meaningful and successful, we need effective planning in the following areas:
- Financing, Staffing, Resources, Motivation, Development, Supervision, Evaluation
Approaches to Educational Planning:
System Approach:
- System Approach was formed by Chester I. Bernard, Herbert A. Simon, 1960.
- This approach focuses on the interconnection and inter-dependence of all the activities in an organisation.
- Thus, system approach refers to a group of inter-linked units. A group of different units forms a complete unit which is known as a system and each small unit is called a sub-system.
- As per system approach, the organisation is a system and various departments within an organisation are its subsystems.
- All the departments should function as a union so that the objectives of the organisation can be achieved.
Contingency or Situational Approach:
According to this approach, the decision-making by the managers should be done according to situations rather than according to principles. Thus, there is no such single formula or principle which can be
applicable in case of all the situations. This is because of the fact that the nature of
environmental factors in an organisation changes every now and then. These
environmental factors can be both internal as well as external factors.
The internal factors are those which exist within an organisation such as policies, objectives, structure of the organisation, etc. On the other hand, the external factors are those which prevail in the outside environment such as competition, suppliers, legal and political system, government policies, etc. The business environment is called dynamic because all internal and external factors are likely to change. Thus, this approach provides suggestions to the managers for the identification of techniques and methods which can be applied in a particular situation so the goals of an organisation can be attained
Manpower Planning Approach:
- In this method, the general demand and the capacity of supply of human resources in different streams and at different levels of the educational sector are estimated.
- The approach asserts that the system of education produces the right quality of human resources with desirable knowledge, attitudes and skills in the right numbers and thus, education is directly linked with economic development.
- The application of the manpower planning approach depends on these factors:
- An appraisal and analysis of the existing employment conditions and the system of education.
- Planning the system of education.
- Using the financial resources (which are limited) in an optimum way so as to fulfill the demands of the employment sector without incurring wastage on account of unemployment.
- Making an appraisal of the number of students enrolled, the number of existing teachers and their qualifications, enrollment in teacher education institutions (availability of future teachers), as well as the existing number of school buildings, equipment, infrastructure and other facilities.
- The requirements of the employers regarding occupational and/ or professional qualifications for employees, their levels of training and abilities should also be assessed.
Institutional planning:
National Level:
- To create conducive conditions for development of nation.
- To provide suitable means for exploitation and utilization of a nation’s
natural, physical and financial resources required for efficient and committed
manpower. - To facilitate human resource in generating high standard of living by
inculcating such skill, attitudes and values which are required for speeding up
the process of economic and educational growth.
Organizational Level:
- Human Resource Management (HRM) is a relatively new approach to manage
people in any organisation. - People are considered the key resource in this approach. It is concerned with the people dimension in management of an all other sub-system of an organization.
- The functional ability and efficiency of people in all subsystems of an organization heavily rely on the policies, programmes and practices of the HRM.
Professional level:
Effective management of human resource will help to improve the quality of
work life. It will promote teamwork among employees by providing a healthy
working environment. It can contribute for professional growth in the following
ways:
a) Providing maximum opportunities for personal development of each employee.
b) Maintaining healthy relationships among individuals, and different work groups.
c) Allocating work properly.
Social Level:
Sound human resource management will have a great significance for the
society. It can help to enhance the dignity of labor in the following ways:
a) Providing suitable employment that provides social and psychological
satisfaction to people.
b) Maintaining a balance between the jobs available and the jobseekers in terms
of numbers, qualifications, needs and aptitudes.
c) Eliminating waste of human resources through conservation of physical and
mental health.
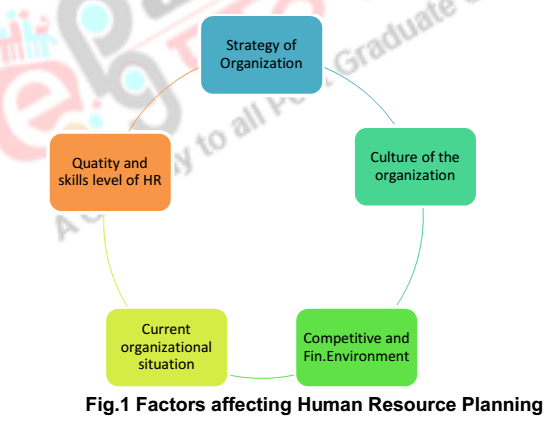
- The human resource executives are now focusing on how human resources can provide
assistance to the organization in achieving its strategic goals. - Thus, HR must now be highly involved in the strategic planning process. Strategic plan is the process by which top management determines overarching organizational objectives and how they can be
achieved. - Its new importance stem from adequately recruited, selected , supervised, inducted and adequately rewarded, provided for, properly developed, employee appraised and promoted on the job.
- Strategically, human resources must be viewed in the same context as the financial, technological and other resources that are managed in an organization.
Significance:
- Human resource management helps in spotting the exact individual for the precise job. Suitability for the job and quality of work go hand in hand in determining the quality of any work force.
- Human Resource Management helps in creating better rapport between the management and the subordinates. It helps subordinates to realize individual and organizational goals.
- Since employees are constantly trained, they are ready to meet the job requirements. The institution is also able to identify potential employees who can be promoted in the future for the top level jobs. Thus one of the advantages of HRM is preparing people for the future.
- If proper recruitment and selection methods are followed, the institution will be able to select the right people for the right job. When this happens the number of people leaving the education organization will be reduced as they will be satisfied with their job leading to decrease in staff turnover.
- Due to proper Human Resource policies, employees are trained well and this makes them ready for future promotions. Their talent can be utilized not only in the educational organization in which they are currently working but also in other institutions
- Political philosophy has undergone change all over the world. The new approach is to develop human resource properly for ensuring its better use. The technological changes have necessitated the use of sophisticated machines.
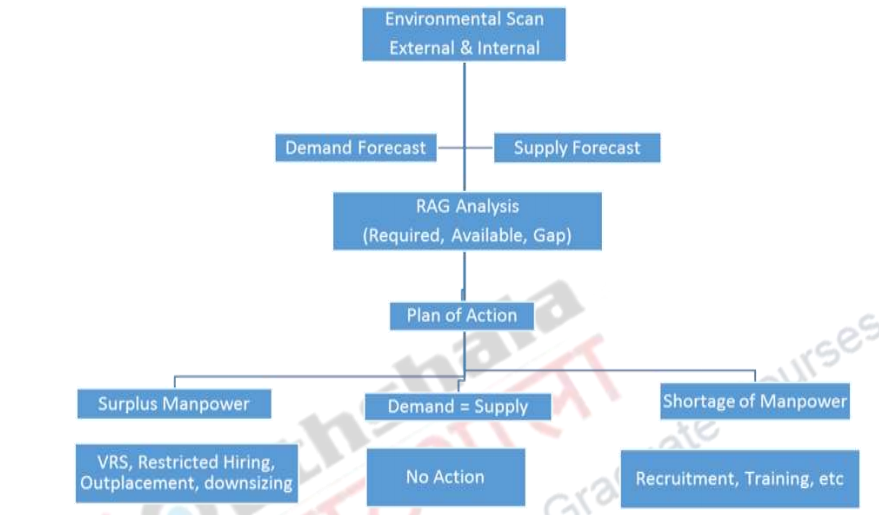
Forecasting Manpower needs:
- Educational administration is primarily a social enterprise as it is more concerned with human resources than with material resources
- supervision should be a cooperative enterprise in which everyone has the right to contribute.
- with the expansion of the enterprise, adoption of complex technology and professional management techniques, the process of human resource planning has assumed greater significance.
- It consists of the following stages:
Analysing organizational plans and deciding objectives:
- The process of human resource planning of an organisation should start with analyzing the
organizational plan. - Analysis of organizational plans and programmes help in forecasting the demand for human resource as it provides the quantum of future work activity.
- The objective stated in economic terms would incorporate the growth rate of the enterprise, diversification plans, market opportunities and government policies. Therefore man power planning
- should meet two requirements.
- It should be directly related to essential nature of the organisation
- The changes in the selected factors should be proportional to change in the human resources required in the organisation.
Analysing factors for manpower requirements:
1. Demand forecasting : Forecasting the overall human resource requirements in
accordance with organizational plans.
Demand forecasting is the process of estimating the future requirements of manpower by function
and level of skills. It has been observed that demand assessment for operative personnel is not a problem but projections are difficult. Two kinds of forecasting techniques commonly used are Judgemental forecasts, Statistical projections
Judgemental forecasts : Judgemental forecasts are conventional methods that involve judgement of those managers and executives who have intensive and extensive knowledge of human resource requirements. It is of two types
a. Managerial Estimate(Expert opinion) : The managers or supervisors who are well experienced with workload, efficiency and ability of employees and decide on the number and type of human resources.
b. Delphi method: A survey approach can be adopted with the Delphi technique. The Delphi
process requires a large number of experts who take turns to present their forecast statement with possible assumptions.
Statistical projections
Some forecasting techniques are based on statistical methods such as ratio trend analysis, Econometric model and work study techniques.
1. Ratio trend Analysis : This is carried out by studying past ratios and forecasting ratios for the future. The components of the internal and environmental changes are considered while forecasting future ratios.
2. Econometric Model : The previous data is analysed and the relationship between different
variables in a mathematical formula is developed. The mathematical formula developed is
applied to forecast of movements in the identified variables to produce manpower
requirements.
3. Work Study Technique(Nominal group method) :
These are generally used to study work measurement. Under the workload analysis, the future workload is analysed and is suitable when the work load is measurable. The work study technique takes into account the productivity pattern for the present and the future, internal mobility of the workers like promotion, transfer, external mobility of the employees like retirement, deaths and voluntary retirements.
2. Supply forecasting :Obtaining the data and information about the present inventory of human resources and forecasting the future changes in present human resource inventory.
- The supply forecasting includes human resource audit , employee wastage, changes due to internal promotion and working conditions.
- The first step is to forecast the future supply of human resource and obtain the present human resource inventory.
Human Resource Audit : The first step includes analysis of each employee’s skills and
abilities. This analysis facilitates the human resource planners with the understanding of
the available skills and abilities of the employees. These job inventories must be updated
periodically in order to avoid employees being ignored for job openings within the
organisation.
Employee Wastage : The second Step is estimation of future losses of human resources of
each department and the entire organisation. This is done to identify the employees who
leave the organisation and to forecast future losses likely to occur such as retirements,
layoff, dismissal, disablement, ill health and death. Reasons for high labour turn over,
absenteeism should be analysed and remedial measures need to be taken.
Internal promotions and working conditions: Analysis is undertaken regarding the
vacancies likely due to retirements and transfers and the employees of particular groups
and categories which are likely to be promoted.
Developing a Human resource Plan:
- Net human resource requirements in terms of number and components are to be determined in
relation to overall human resource requirement. - After determining supply and demand of the employees, the management starts adjustment. When the internal supply of the employees is more than the demand, human resource surplus exists.
- And the external recruitment is stopped. Besides this, the existing employees are encouraged to take voluntary retirement. . It gradually reduces surplus. If human resource deficit exists then the planners have to rely on the external source of recruitment.
Manpower planning:
- HR planning requires two types of information: data from the outside environment and data
from inside the organization. - Data from the outside environment include information on present conditions and foretold changes in the general economy, and the economy of the particular industry, the relevant technology, and the competition. Any of these factors may influence the organization’s business plans and thus the requirement for human resources.
- The second type of information is available in the organization. Inside information contains both short and long-term plans and strategies of the organization, current state of human resources in the organization. Once the information from the outside and inside sources is accumulated, planners can forecast the future demand for employees, supply of labor from internal and external sources.
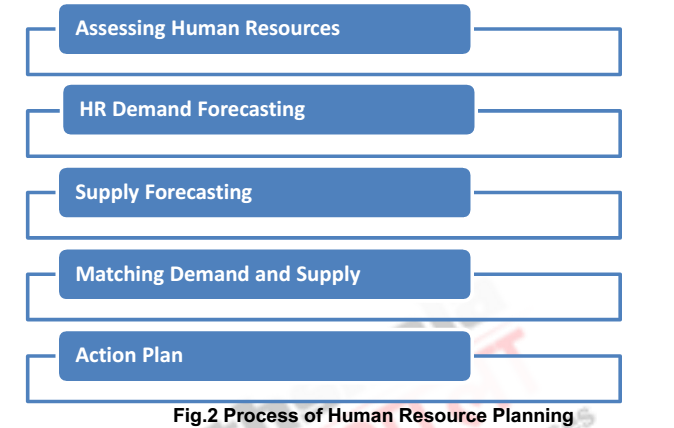
Assessing Human Resources:
- The evaluation of HR begins with the analysis of environment- external and internal,
outside environment contains the political, economic, social and technological
variables and internal environment consists of objectives, resources and structure to
assess the currently available HR inventory. - Once the analysis of external and internal forces of the organization is done, HR manager finds out the internal strengths and weakness of the organization on the one hand and opportunities and threats for the organization on the other.
HR Demand Forecasting:
- Demand forecasting is a process of ascertaining future needs for human resources.
- It is carried out to fulfill the future personnel requirements of the organization to obtain the desired level of output.
- Future human resource needs can be estimated with the help of the organization’s current human resources and analysis of organizational plans and procedures.
- It will be essential to conduct an analysis for every significant level and type of personnel every year.
- Mathematical methods consist of productivity ratio, learning curves, multiple regression and linear programming.
Supply Forecasting:
- It is the process of anticipating availability of human resources followed after demand for testing of human resources.
- Internal supply of human resources is available by way of transfers and promotions of existing employees, retired employees & calling laid-off employees, etc.
- Sources of external supply of human resource consist of labor force at hand in the market and the pool of labor force available for new recruitment.
Matching Demand and Supply:
- The corresponding process refers to bring demand
and supply to a position of equilibrium so that shortages and surplus position will be
avoided. - In case of shortages an organization has to recruit more employees. On the other hand, in the case of over staffing it has to bring down the existing employment.
- Therefore, this matching process gives knowledge about requirements and sources of HR.
Action Plan:
- The final phase of human resource planning is concerned with finding out the surplus
and shortages of human resource. - In this phase the HR plan is implemented through the designation of different HR activities.
- The main activities required to bring into action the HR plan are
- recruitment, selection, induction, training and development
and socialization etc. - Finally, the control and evaluation of performance of HR to
check there are fit between HR planning and the HR objectives and policies follows.
This action plan need be updated with the change in time and conditions.
- recruitment, selection, induction, training and development
Benefits of Manpower planning:
- Manpower planning has gained wide recognition as a reliable tool for effective human
resource management. In recent times, even the medium and small organisations have realized
the critical role of human resource planning in goal accomplishment and cost reduction.- Human resource planning helps the organisations in utilizing human resources better through effective planning and timely execution.
- It assists the organisations in anticipating the future trends in the demand and supply of labour
- It replaces the haphazard and thumb rule approaches towards human resource management with a well planned, systematic and scientific approach.
- It forms the basis for al Human resource activities including recruitment, training, performance appraisal, compensation fixation and employee retention.
- Human resource plans are capable of serving both long term and short term HR requirements of the organisation.
- It facilitates industrial relations by information sharing between the management and labour unions.
- It helps the organisation in determining the career growth of each employee in a systematic manner.
- It helps the organisation in creating and maintaining a satisfied , well trained and skillful work force.
Limitations of Manpower planning:
- The projection of manpower requirements against demand and supply may be risky and
inaccurate - Technological changes and market fluctuations are uncertain
- Lack of support from management
- Human resource planning mainly considers the quantitative aspect and ignores the
qualitative aspects such as motivation, career prospects, training and so on - Employees resistance exists and they feel that it increases work load
- Employers also do feel human resource planning increases the cost of manpower.
- Man power planning is a time consuming and expensive exercise
- Inefficient information systems with absence of reliable data will fail to develop effective
human resource plans
Recent Comments