The structure of arguments:
- The following refers to an attribute of every categorical proposition which is determined by whether the proposition affirms or denies class inclusion?
- quality
- quantity
- distribution and
- comparison
- In the figure of categorical syllogism quantity and quality of a proposition determine Mood of the syllogism.
- True statement with respect to the first figure of categorical syllogism – Middle term is the subject of the major premise and the predicate of the minor premise.
- The characteristics of the middle term
- It must be present in the minor term
- It must be present in all positive instances in which the major term is present
- It is drawn from the preceding propositions
- The characteristics of the middle term
- All students cleared their examination and few students did not clear their exams. This is an instance of Contradictories.
- Contradictory statements has different quantity and quality.
- Some students are sincere is an example of a ——– proposition.
- particular affirmative
- In a proposition which is particular affirmative Neither the subject nor the predicate is distributed.
- particular affirmative
- “All tigers are animals” this is an example of which type of proposition
- Universal affirmative
- Universal affirmative propositions distributes subject alone
- Universal affirmative
- In which of the following propositions both can be true simultaneously but cannot be false simultaneously
- sub-contrary and
- Some animals are fierce
- some animals are not fierce
- Sub-contrary propositions.
- sub-contrary and
- Converse of ‘some S is P’ –
- Some P is S
| Proposition | Converse | True/False |
| All S are P | some P are S | T |
| No S is P | No P is S | T |
| Some S are P | Some P are S | T |
| Some S are not P | Some P are not S | F |
- S1: Some chairs are curtains,
- S2: All curtains are bedsheets
- Conclusion: some chairs are bedsheets.
- The mood of the above proposition – IAI
- With reference to proposition, some girls are not students. Identify the correct statements:
- predicate students are distributed.
- subject girls are undistributed.
- Some birds are mammals is a particular affirmative proposition and it distributes neither subject form nor predicate term.
- In affirmative propositions, the predicate term is always taken particularly and therefore undistributed.
- As per classical square of opposition, if A proposition is true the following is correct,
- E proposition is false and I proposition is true and O proposition is false.
- The following proposition is Contrary to ‘All poets are dreamers’
- No poets are dreamers.
- Between 2 universal propositions having the same subject and predicate but differing in quality only
- True = A+I – Affirmative statements, False = E+O – Negative Statements.
- The following combination of proportions is considered to be contraries in the classical square of opposition?
- Universal affirmative and universal negative
- If two propositions are related in such a way that they cannot be true together although both may be false together then such a relation is considered to be Contrary.
- All poets are dreamers – No poets are dreamers
- The statements which are correct with reference to the deductive argument?
- the relation between premises and conclusion is of logical necessity
- Consider the following statements and choose the right option
- Middle term should be distributed in at least one premise.
- If it rains then the drought will end. The drought has ended. Therefore it rained Which kind of fallacy does this commit?deductive fallacy.
- It is a pattern of reasoning rendered invalid by a flaw in its logical structure
- Not a part of immediate deductive inference – syllogism
- Others include
- conversion
- Obversion
- Contraposition
- Others include
- Which one of the following is the characteristics feature of an argument?it is either valid or invalid
- Truth or falsity is related to proposition of statements involved in arguments.
- The converse of ‘all cats are mammals’ is some mammals are cats.
- two statements which are in such a relation that the truth of one implies the truth of the other, but not conversely.
- All plastics are synthetic.
- Some plastics are synthetic.
- two statements which are in such a relation that the truth of one implies the truth of the other, but not conversely.
- In this statement “No dogs are reptiles” which terms are distributed?
- Both subject and predicate terms.
- According to the traditional square of opposition, if two proposition is related that they cannot both be false, although they both be true is called sub-contraries.
- True statement – Some birds are mammals is a particular affirmative proposition and it distributes neither subject form nor predicate term
- Distributes Subject alone – All poets are dreamers
- Distributed predicate – Some girls are not students
- Distributes both subject and predicate – No dogs are reptiles
- If ‘a’ is inversely proportional to ‘b’ and ‘b’ is inversely proportional to ‘c’ then’a’ is inversely proportional to c
- ‘a’ is directly proportional to ‘c’
- The product of any 3 consecutive integers is divisible by 6. Therefore 3*4*5(-60) is divisible by 6? which type of reasoning is embodied here?
- deductive reasoning
- 2 premises with 4 conclusions drawn from them. The valid conclusion drawn from the premises
- premises:
- all diaries are copies
- No copy is a book
- conclusion:
- No book is copy
- No diary is book
- The middle term ‘book’ is the subject of the major premise and the predicate of the minor premise.
- Book is distributed in at least one premise.
- premises:
Indian Logic:
- The term ‘paksa’ according to the classical Indian school of logic refers to the following terms in the process of inference.
- Minor term
- Sandhya is the major term, hetu is the middle term.
- Paksa further classified as sapaksasattva and vipaksasattva.
- Eg. The hill has fire because it is knowable – paksa is fire.
- Minor term
- The distinction between savikalpaka (determinate) and nivikalpaka(indeterminate) is made with respect to which of the following pramanas?
- pratyaksha (perception)
- The term yogaja (intuitive) pertains to the following pramana perception.
- The distinction between laukika and alaukika is made with reference to the following pramanas – pratyaksha (perception)
- Identify the distinctive feature of traditional method of indian education from the following list:Direct perception of truth – both as means and end.
- According to Nyaya philosophy:
- Pratijna – the logical statement to be proved – The hill is fiery.
- Hetu – Because it has smoke – It states the reason for the establishment of the proposition
- Udharana – Whatever has smoke has fire – e.g., an oven – Gives an universal concomitance with with an example
- Upanaya – This hill has smoke, which is invariably associated with fire – application of universal concomitance together with an example
- Nigamana – Therefore the hill is fiery – It is the proved conclusion
- According to Nyaya philosophy:
- Which of the following is not correct with reference to anumana according to the classical Indian school of logic?
- Hetu is the minor term
- Others which belong to anumana are
- Hetu is the middle term gives statement of reason.
- Paksa is the minor term gives predicate
- Sandhya is the major term gives subject
- the following is signified by the term ‘hetu’ in the process of anumana(inference) in the classical Indian school of logic?
- statement of reason – The logical statement to be proved – Pratijna – This hill has fire.
- The attributes shared by all and only those objects in which a term refers is known as
- the intention of a term
- connotation
- The following pramanas is used by classical Indian school of logic to prove the existence of god?
- Inference (anumana)
- sadharana: middle term is too wide that is present in both vipaksha (negative instance) and sapaksa(positive instance).
- The hill has fire because it is knowable, where knowable can be present both in fiery and non-fiery objects.
- sattpratipaksha:
- Here the middle term is contradicted by another middle term. sound is eternal, because it is audible’ and ‘sound is non-eternal, because it is produced. Here ‘audible’ is counter-balanced by ‘produced’ and both are of equal force.
- Reference
- Vyapti – relation of invariably concomitant between major and middle terms in anumana
- smoke(major) in the hill(minor) means there is fire(inferred – vyapti)
- Eg. Wherever there is smoke, there is fire – The relation of invariably concomitance between fire and smoke.
- Inference (anumana)
- According to the classical Indian school of logic the correct sequence of steps involved in anumana(influence) –
- Pratijna, Hetu, Udharana, Upanaya, Nigamana
- The following fallacies hetu (middle term) is not uniformly concomitant with the major term –
- Saryabhicara(irregular middle)
- Asiddha: fallacy of unproved middle. The middle term must be present in minor term(paksadharmata).If not it is unproved
- Rule: Middle terms present in minor term(pakshdharmatha) but in asiddha fallacy occurs as middle term not present in minor term.
- Sattpratipaksha (Inferentially contradicted):
- The middle term is contradicted by another middle term. The reason is counter-balanced by another reason. ‘sound is eternal, because it is audible’ and ‘sound is non-eternal, because it is produced’. Here ‘audible’ is counter-balanced by ‘produced’ and both are of equal force
- “Fire is cold, because it is a substance” is an instance of which one of the fallacy of inference –
- Asiddha (unproved middle term)
- Badhita (non-inferentially contradicted middle)
- Virudha(contradictory middle)
- Savyabhichara(irregular middle)
- Asiddha – When the middle term is not present in minor term. Eg. sky lotus is fragrant because it is like the lotus in the pond.
- Badhita – Eg., fire is cold, because it is a substance’. Here the middle term ‘substance’ becomes contradicted because its major term ‘coldness’ is directly contradicted by perception.
- Viruddha – The hetu or middle term condradicts itself, sound is eternal, because it is produced – Here ‘produced’, instead of proving the eternality of sound, proves its non-eternality
- satpratipaksha (Inferentially contradicted) – It occurs when middle term is contradicted by another middle term. eg. Sound is eternal because it is audible.
- Savyabhichara: It is not uniformly concomitant with the major term. So,the middle term fails to prove the conclusion as it gets associated with vipaksasattva and sapaksasattva (positive and negative minor term).
- Devdatta is fat and does not eat during the day. Therefore, Devdatta is eating during the night. This example suits which Indian school of logic –
- Implication(Arthapatti)in indian logic Assumption of unpercieved fact under two apparently inconsistent perceived facts is arthapati(Implication or postulation).
- unpercieved fact – Devdatta is fat and does not eat during the day.
- Perceived fact – Therefore, Devdatta is eating during the night.
- Which one of the following is signified by udharan of anumana(inference) in Indian logic?
- Universal proposition along with an instances
- The following is true with reference to anupalabdhi as a means of knowledge?
- One do not cognize the pot on the table, therefore, it is absent there.
- Assumption of unpercieved fact inorder to reconcile two apparently inconsistent perceived facts is known as Indian logic?
- Arthapatti(Implication)
- Eg. Devadatta is growing fat. He does not eat food during the day.
- Therefore, He must be eating food during the night, other things being equal.
- With reference to the Indian school of logic, the following is
- It is related to the form of the argument only.
- It is related to the content of the argument only.
- In the age of Vedas students were admitted to the Vedic schools after the performance of which ceremony among the following? upanayana ceremony
- The following is not a necessary step when you present an argument based on inference before the others according to the classical Indian school of logic?
- Upamana – Upaman (comparison) comes under the pramanas which is the basis of acquiring knowledge.
- Pramanas includes – Pratyaksha, Anumana, Upamana, Arthapatti, Anuplabdhi and sabda.
- Under anumana there are five modes of inference which are as follows.
- Pratijna – This hill has fire
- Hetu – Because it has smoke
- Udharana – Whatever has smoke has fire, e.g., an oven.
- Upanaya – This hill has smoke which is invariably associated with fire.
- Nigamana – Therefore this hill has fire
- Upamana – Upaman (comparison) comes under the pramanas which is the basis of acquiring knowledge.
Mathematical Reasoning:
- Given below is a question followed by 3 statements identify the statements (a,b,c) that are necessary to answer the question.
- What is the avg of students studying in a class?
- boys and girls in the class are in the ratio 7:8 the average age of boys and girls are 12.3 and 11.4 yrs the number of boys in the class is two less than the number of girls in the class
- b and either a or c
- If A is directly proportional to B; B is inversely proportional to C and C is directly proportional to D then
- A is inversely proportional to D
- A is inversely proportional to C
Verbal Reasoning:
- Apoorva is the son of Madhu. Vinod is the brother of Madhu’s husband how is apporva related to Vinod? –
- nephew
- Uncle
- brother
- Cousin
- A is the father of B and C is sister of A. D is the grandson of C. How is D related to B?
- Uncle
- nephew
- cousin
- grandson
- B is the only daughter of maternal grandmother of A. How is A related to B?
- daughter,
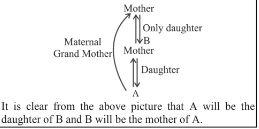
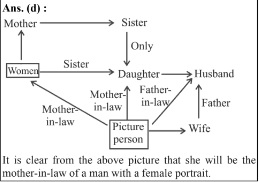
- Pointing towards a man a woman said ” his wife’s father is the husband of my mother’s only daughter” How is the woman related to the man?
- Mother in law
- A question followed by 3 statementsthe statement which is necessary to answer the question. What is the speed of the train?
- The train crosses another train running in the opposite direction in 20 seconds
- the train crosses a platform of length 300m in 30 seconds
- the train crosses a pole in 10 seconds
Letter series:
- If ‘solution’ is R5KTSH5M’ then ‘CROME’ will be written as
- BQ5LD
- ENGLAND code as ULSNYLV so code for IRELAND –
- QHUNYLV
- Method-1:
- By comparison of the word ENGLAND and IRELAND – these words are similar – ELAND so – coded words UNYLV
- EN in england and IR in ireland are in a proper alphabetical sequence while in the code it has to be reversed.
- Method -2:
- Opposite letter – 1 = V-1 = U (Reverse order addition of alphabet is negative)
- E(5) = V(5) from inverse – 1 = U, G(7) = T(7) – 1= S
- Rule: The letters of the given word ENGLAND are coded 1 less than the reverse order letter.
- Reference:
- Method -2:
- QHUNYLV
- The next term in the series AT, EQ, IN, OK,……is UH.
- Normal order, A+4 = E+4 = I+6 = o + 6 = U
- Reverse order, K+3 = N, N+3 = Q, Q+3 = T, So, H+3 = K
- Choose the missing term out of the given alternatives: QPO, NML, KJI, _______.
- HOF
- The next term of the series 1D3, 3IH5, 5L7,———
- 7P9
- 1+2 = 3, D(4)
- 3+2 = 5, H (8)
- 5+2 = 7, L(12)
- The following sets of letters when sequentially placed at the gaps in the letter series below shall complete it? bb_b_ab,cbba_bcbb_
- cbbba,
- bb comes together and in space a or c,
- so the series will be bba,bbc
- Hence, bbc/bba/bbc/bba
- In a certain code, CREDIT is written as “EPGRKR” and in the same code DEBIT will be FDCGV
- FGCDV
- C+2 = E, R-2 = P, E+2 = G, D-2 = B.
- Coding language – ‘AEIOU’ is written as ‘TNHDZ’ So, BFJPV is written as UOIEA
- A(1), E(5), I(9), O(15), U(21) , so reducing 1 letter in a reverse order T(20), N(14), H(8), D(4), Z(26),
- So, B(2), F(6), J(10), P(16), V(22) as UOIEA
- If HPU = 9, JNU=9, then DU =
- 5
- If the word teacher is coded as TCJACCV and the word SURGEON is coded as PMGETSU in a certain code language. then which of the following will represent the word CONCORD in that language
- TEACHER – reverse of TCJACCV
- T+2 = V, E-2 = C,A+2 = C, C-2 = A, H+2 = J,E-2 = C, R+2=T
- Similar pattern, SURGEON and it’s reverse USTEGMP
- Hence, CONCORD is coded as FPQAPME
- TEACHER – reverse of TCJACCV
- Coding language – ‘AEIOU’ is written as ‘TNHDZ’ So, BFJPV is written as UOIEA. Corresponding alphabets in inverse – Z-A, D-E, H-I, N-O, T-U
- Similary for B-A, F-E,J-I, O-P, U-V writting next element in reverse order
Fallacies of inference:
- A fallacy in which an opponent position is depicted at being more extreme or unreasonable than is justified by what was actually asserted is called
- straw man
- A strawman’s argument is a cheap and easy way to make one’s position look stronger than it is. Using this fallacy opposing views are characterized as “non-starters”, lifeless,truth less and wholly unreliable. Reference:
- Eg. “When the U.S Senator thinks we can solve all our ecological problems by driving a hybrid electric car”“Quite the contrary, he also thinks the environment is such a wreck that no one’s car choice or driving habits would make the slightest difference.”
- Red herring: It is a kind of argument that tend to deviate from the core subject of the debate.
- when Dr. Apj abdul kalam is questioned by top journalist of the nation he said to them that he came to talk about national development not to answer any personal agenda. Thereby avoiding distraction of the world.
- ad hominem: A personal attack is called ad hominem that often is contrary to rational arguments. Recently tamil actor Rajini talks about periyar that attracts comments from politicians to attack his personal life and family. They states that he is wrong and undisciplined by nature.
- Argumentum ad baculum(fear of force) fallacy committed when one appeals to force or the threat of force to bring about the acceptance of a conclusion.
- A strawman’s argument is a cheap and easy way to make one’s position look stronger than it is. Using this fallacy opposing views are characterized as “non-starters”, lifeless,truth less and wholly unreliable. Reference:
- straw man
- “Everyone is going to the party you should go too” This inference commits which kind of fallacy
- ad populum
- Bandwagon fallacy(ad populum) is when something is accepted because all other people agrees on it.
- Equivocation (ambiguity) – when a word, phrase, or sentence is used deliberately to confuse decieve, or mislead it’s saying one thing but actually saying something else. However equivoction tone has a tone of deception instead of just a tone of misunderstanding
- Ad ignorantiam:Ignorance is used as a major prmise in an argument it is liable to be fallacious appeal to ignorance. –
- No one has ever been able to prove definitively that extra-terrestrials exist, so they must not be real.” No one has ever been able to prove definitively that extra-terrestrials do not exist, so they must be real.”
- So An appeal to ignorance isn’t proof of anything except that one don’t know something.
- The inference “A mouse is an animal. Therefore a large mouse is a large animal commits which of the following fallacies
- equivocation
- An informal fallacy in which the conclusion of an argument which is stated
- Begging the questions
- circular argument
- pelitin principii
- Circular argument (petitio principii) – If someone says, “The Bible is true; it says so in the Bible”e – No new conclusion- circular arguments is that they start where they finish, and finish where they started.
- Begging the question — A kind of presumptuous argument where it only appears to be an argument. It’s really just restating one’s assumptions in a way that looks like an argument. Conclusion also appears as one of the premises in the argument.
- In this hospital, some nurses don’t wear white dress some doctors have private practice and medicines prescribed are of the high cost. Therefore treatment in this hospital is of poor quality. What fallacy does this argument make?
- slippery slope
- Slippery slope: One predicted the outcome of quality of a hospital just by noting the fact about nurses, doctors and medicines.
- The strawman argument is often accidental that the offender oversimplifies or discredits their opponents views during the heat of the debate.
- fallacy of composition occurs when one infers that is something is true of some part of a whole, it must be a true of the whole
- fallacy of division occurs due to reasons that something that is true of a whole must be true for some or all of its parts.
- Mr.X lives in a slum and is unemployed. Therefore Mr. X deserves to be a minister -The kind of fallacy in this argument is
- Ad misericordia – Like the ad hominem the fallacy appeals to compassion and emotional sensitivity of others when these are irrelevant for a rational argument. When one appeals to pity it appears to be emotional manipulation.

Recent Comments