Passive transport:
- True statements about passive transport
- Substances move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
- In passive transport, molecules always move along the concentration gradient, from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
- Substances move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
- Some substances such as sugars, amino acids, and ions move across the cell membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration using special proteins embedded in the membrane. Which of the following terms applies to this type of cell transport?
- Facilitated diffusion
- In facilitated diffusion, molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channel proteins and carrier proteins.
- Facilitated diffusion
- Which of the following substances is unable to diffuse across the plasma membrane?
- Sodium, because ions have charge.
- Although sodium ions are small, their charge prevents them from moving across the cell membrane through simple diffusion. They must be transported by special proteins through the process of active transport.
- Water molecules are able to diffuse across the cell membrane via the use of protein channels called aquaporins.
- Oxygen is not polar.
- Carbon dioxide is small enough to diffuse easily across the cell membrane.
- Sodium, because ions have charge.
- Which of the following is true regarding the proteins involved in facilitated diffusion?
- Channel and carrier proteins transport materials at different rates.
- Channel proteins are able to transport molecules much more quickly than carrier proteins because channel proteins act as simple tunnels. Carrier proteins must change shape and “reset” each time they move a molecule, which takes more time than simply allowing molecules to pass through a channel.
- Aquaporins are channel proteins that span the membrane allowing water to cross the membrane very quickly through a hydrophilic tunnel.
- Although sodium, potassium, and calcium ions are generally quite small, their charge prevents them from moving across the cell membrane through the use of channel proteins. Instead, they must be transported through the ATP-requiring process of active transport.
- Channel and carrier proteins transport materials at different rates.
- Starch turns a blue-black color in the presence of iodine. Julian decides to use this information to test the permeability of some dialysis tubing. Julian fills the tubing with a starch solution and places it in a beaker of iodine and water. After two hours, the starch solution in the dialysis tubing turns blue-black. The iodine solution remains the same color (it doesn’t change colors). What do Julian’s results show about the permeability of the tubing?
- The dialysis tubing is permeable to iodine but not to starch.
- Because starch will turn blue-black in the presence of iodine, and the dialysis tubing changed color, we know that iodine must have gotten into the dialysis tubing to combine with the starch solution. This means that the tubing must be permeable to iodine.
- Similarly, if the dialysis tubing was permeable to starch, starch would have diffused across the tubing into the beaker, changing the color of the iodine solution. We know from the problem that this did not occur. This means that the tubing was not permeable to starch.
- The dialysis tubing is permeable to iodine but not to starch.
Active transport:
- Which way do particles move during active transport?
- From areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration
- Active transport moves particles against their concentration gradient, from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration.
- From areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration
- the following forms of transport uses ATP directly
- Active transport requires the use of energy (usually in the form of ATP).
- Osmosis occurs passively, without the help of ATP or other energy molecules
- Facilitated diffusion is a passive process, so energy molecules like ATP are not needed.
- During cell respiration, the reactants of glucose and oxygen are transformed into the products of carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. Which of the following cell transport processes would be most negatively impacted if a cell no longer had access to oxygen?
- The transport of glucose against its concentration gradient in a small intestinal cell.
- This is an example of active transport because it’s going against the concentration gradient. Without access to oxygen, ATP can’t form efficiently and therefore, active transport can’t occur.
- The transport of glucose against its concentration gradient in a small intestinal cell.
- During cell respiration, the reactants of glucose and oxygen are transformed into the products of carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. Which of the following cell transport processes would be relatively unaffected if a cell no longer had access to glucose?
- The transport of calcium into a muscle cell via facilitated diffusion.
- This is an example of passive transport that doesn’t need ATP to occur, so it would be unaffected by a lack of glucose.
- Charged molecules like potassium (K+) do not pass through the cell membrane via passive transport.
- Without access to glucose, ATP can’t form efficiently and since this is an example of active transport that requires ATP, it would be severely effected.
- The transport of calcium into a muscle cell via facilitated diffusion.
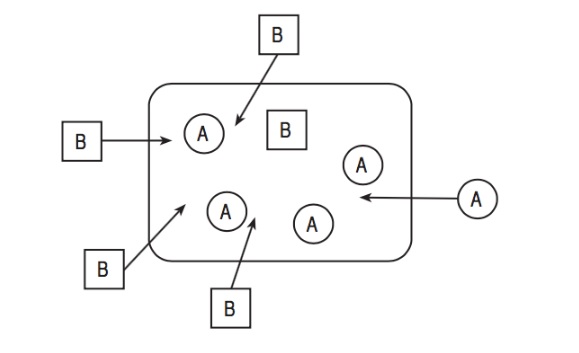
The concentration of substance A is higher inside the cell, so energy is needed to move it against its concentration gradient. This process is active transport.
- Which of the following statements are true regarding active transport and facilitated diffusion?
- Both processes require the use of membrane proteins.
- Active transport utilizes carrier proteins on the cell membrane and facilitated diffusion can utilize either channel or carrier proteins on the cell membrane.
- Active transport moves substances against the concentration gradient and facilitated diffusion moves substances along the concentration gradient.
- Active transport is active because it requires ATP in order to go against the gradient and facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that goes with or along the gradient without the use of ATP.
- Both processes require the use of membrane proteins.
- Dr. Bad has developed a way to damage the ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABC transporter) on a cell. The cell’s ABC transporter can no longer bind and use ATP when it’s transporting substances. Which of the following statements best describes how this damage would affect the transport of substances in the affected cell?
- Substances at a low concentration outside the cell would not be transported into the cell, where there is a high concentration.
- Since the ABC transporter can no longer utilize ATP as an energy source to fuel its function, active transport against the concentration won’t occur.
- Substances at a low concentration outside the cell would not be transported into the cell, where there is a high concentration.
- Which of the following is an example of active transport in a cell?
- Sodium moving out of the cell against its concentration gradient
- Active transport uses energy molecules to move particles like sodium, against their concentration gradients, from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration.
- Sodium moving out of the cell against its concentration gradient
- When would a cell need to use active transport instead of passive transport?
- To take in nutrients that have a lower concentration outside the cell
- Active transport moves particles from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration.
- To take in nutrients that have a lower concentration outside the cell
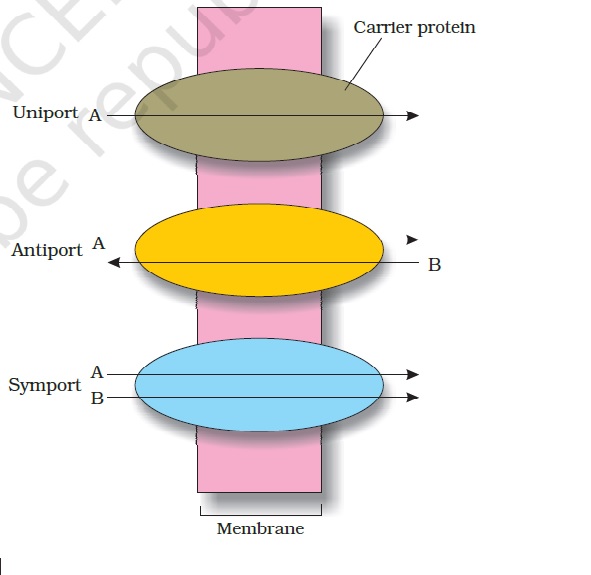
Osmosis and tonicity
- A scientist places human blood cells into an unknown solution. After some time, the blood cells swell and burst. What type of solution were the blood cells likely placed in?
- A hypotonic solution
- Hypotonic solutions contain a higher water concentration and a lower solute concentration compared to a cell’s. The solution in the problem made the blood cells swell and burst, so it has a lower solute concentration than the cells.
- A hypotonic solution
- A scientist places human blood cells into an unknown solution. After some time, the blood cells shrink and shrivel up. What type of solution were the blood cells likely placed in?
- A hypertonic solution
- Hypertonic solutions contain a lower water concentration and a higher solute concentration compared to a cell’s. The solution in the problem made the blood cells shrink and shrivel, so it has a higher solute concentration than the cells.
- A hypertonic solution
- Which of the following is true of osmosis?
- Osmosis is a type of passive transport
- Osmosis is the passive diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration (in other words, an area of high concentration of water to an area of low concentration of water).
- Osmosis is a type of passive transport
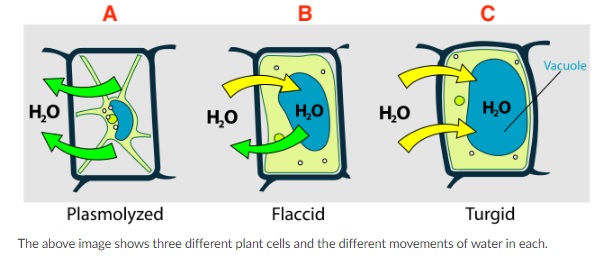
- The below image shows three different plant cells and the different movements of water in each. Which of the following answer choices are true?
- Plant cell A (plasmolyzed) is within a hypertonic solution because water is leaving the cell.
- Plant cell A is shrunken because the concentration of water on the outside of the cell is lower than on the inside. Therefore, water will continuously leave the cell, causing it to shrink and plasmolyze.
- There is a higher concentration of water on the outside of plant cell C (turgid) than on the inside.
- Plant cell C is full of water because the outside solution is hypotonic to the cell. Therefore, the excess water on the outside will move into plant cell C, causing it to swell, or become turgid.
- Because water is both entering and exiting plant cell B, the concentration of water on the outside of the plant cell must be equal, or isotonic, to the concentration of the cell.
- Plant cell A (plasmolyzed) is within a hypertonic solution because water is leaving the cell.
- A cell has a 1% salt concentration. It is placed into a solution containing a 10%salt concentration. What will happen to the cell?
- Water will move out of the cell, causing it to shrink.
- The cell has lower concentration of solute and a higher concentration of water than the solution it is placed in. This means that water will move out of the cell, causing it to shrink.
- Water will move out of the cell, causing it to shrink.
- The diagram below represents what occurs when plant cell is placed into an unknown solution.
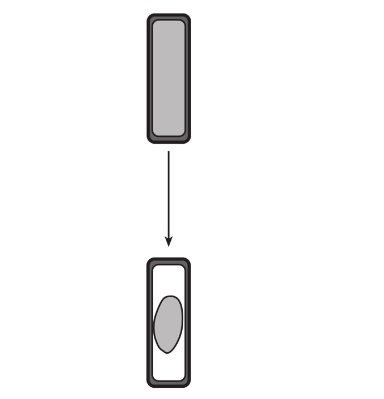
- Based on what happened, what type of solution was the cell placed in?
- A hypertonic solution
- In the solution, the cell shriveled. This means the cell was placed in a solution containing a comparatively lower water and higher solute concentration. Water moved from inside the cell to out of it, causing the cell to shrivel.
- A hypertonic solution
- A cell has a 2% salt concentration. It is placed into a solution containing a 2%salt concentration. What will happen to the cell?
- Water will move into and out of the cell at the same rate, causing it to remain the same size.
- Both the cell’s salt concentration and the solution’s salt concentration are 2% meaning that the cell is in an isotonic solution. The cell will neither swell nor shrink, but remain the same size.
- Water will move into and out of the cell at the same rate, causing it to remain the same size.
- A cell has a 5% salt concentration. It is placed into a solution with a 0.5% salt concentration. What will happen to the cell?
- Water will move into the cell, causing it to swell.
- The cell has higher concentration of solute and a lower concentration of water than the solution it is placed in. This means that water will move into the cell, causing it to swell and ultimately burst.
- Water will move into the cell, causing it to swell.
- A plant cell has a 5% salt concentration. It is placed into a solution containing a 12% salt concentration. What will happen to the plant cell?
- Water will move out of the plant cell, causing it to shrivel.
- The plant cell has lower concentration of solute and a higher concentration of water than the solution it is placed in. This means that water will move out of the plant cell, causing it to shrivel.
- Water will not move into the plant cell because this would be against the concentration gradient.
- Water will move out of the plant cell, causing it to shrivel.
- When a patient is admitted to the hospital and needs to be placed on intravenous (IV) fluids, its important that these fluids are at an isotonic concentration to their own body’s fluids. If the saline (salt) concentration of the body’s fluids is 0.9% what should be the concentration of IV saline solution administered to a patient?
- 0.9%
- This would be an isotonic IV saline solution since it’s the same concentration that occurs within the body. This is known as normal or physiological saline.
- 0.9%
- Which of the following is true about osmosis?
- It is a type of passive transport.
- Osmosis is the passive diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. It does not require energy to occur.
- It is a type of passive transport.
Diffusion, osmosis, and tonicity:
- Tahira placed a collection of red blood cells into a container filled with an unknown solution. Once in the container, Tahira noticed that the red blood cells swelled and some of them burst. What type of solution were the red blood cells placed in?
- A hypotonic solution
- A hypotonic solution is a solution that contains a higher water concentration and a lower solute concentration compared to another solution. Since the solution in the problem caused the cells to swell and burst, this means that it must have had a lower solute concentration in the cells, causing water to enter them.
- A hypotonic solution
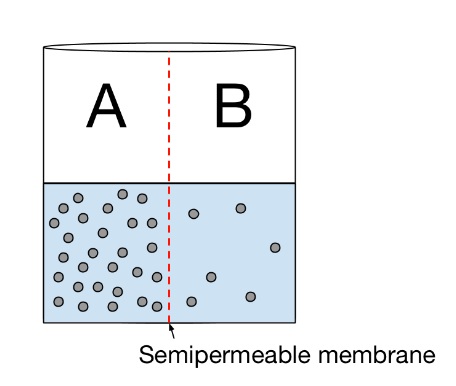
- The figure below shows a beaker filled with water and a solute. The beaker has membrane down the center, which is permeable only to water. Which of the following best describes the way the water will flow through the semipermeable membrane?
- Water will flow into side A.
- Because the membrane is only permeable to water, the solute molecules cannot cross through. Water will move from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration (in other words, an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration). Since the solute concentration in B is lower than the solute concentration in A, water will move from side B to side A to balance out the concentration gradient.
- Water will flow into side A.
- In which direction do particles in a solution move during passive diffusion?
- From higher to lower areas of concentration
- During diffusion, particles will move along the concentration gradient from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration in an effort to reach equilibrium (when the molecules are even throughout a space). This process does not require any energy.
- From higher to lower areas of concentration
- An animal cell has a 2% salt concentration. It is placed into a solution with a 0.05% salt concentration. What will happen to the animal cell?
- Water will move into the animal cell, causing it to swell and burst.
- The animal cell has higher concentration of solute and a lower concentration of water than the solution it is placed in. This means that water will move into the animal cell, causing it to swell.
- Water will move into the animal cell, causing it to swell and burst.
- The image shows atoms of helium gas in a box. The box is divided into two sections of equal volume by a membrane which is permeable to helium. Which of the following scenarios is most likely to occur?
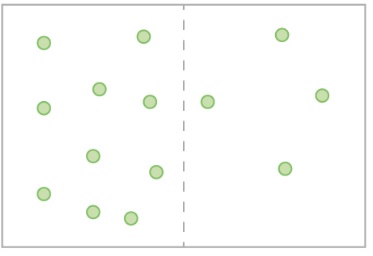
- There will be a net movement of helium atoms from left to right.
- The concentration of helium atoms on the left is higher than the concentration of helium atoms on the right. In an effort to reach equilibrium where the molecules are even throughout the space, the helium atoms from the left side will move along the concentration gradient towards the right.
- The image below shows molecules of carbon dioxide gas in a box. The box is divided into two sections of equal volume by a membrane which is permeable to carbon dioxide. Which of the following scenarios is most likely to occur?
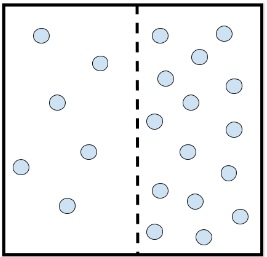
- There will be a net movement of carbon dioxide molecules from right to left.
- In order for this system to reach equilibrium where the molecules are even throughout the space, there must be a net movement of molecules.
- since, The concentration of carbon dioxide molecules on the right is higher than the concentration of carbon dioxide molecules on the left.
- In an effort to reach equilibrium where the molecules are even throughout the space, the carbon dioxide molecules from the right side will move along the concentration gradient towards the left.
- The U shaped pipe shown in the figure below is divided with a membrane that is only permeable to water. Which of the following best describes how water will flow through the membrane?
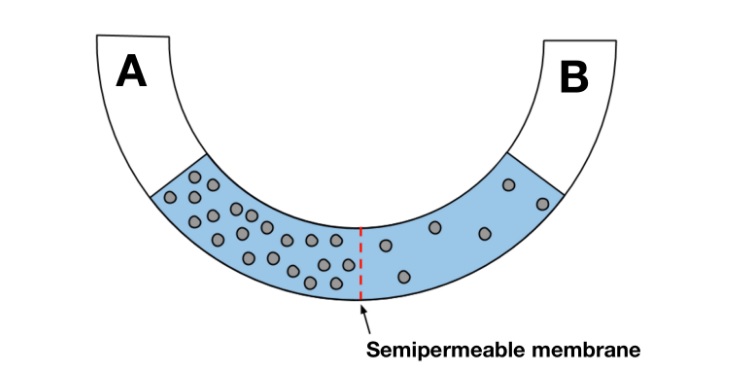
- Water will flow from side B into side A.
- Because the membrane is only permeable to water, the solute molecules cannot cross through. Water will move from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration (in other words, an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration). Since the solute concentration in B is lower than the solute concentration in A, water will move from side B to side A to balance out the concentration gradient.
- Although the water levels appear equal, the respective concentrations are not the same. Side A has a higher solute concentration (or lower water concentration) than side B and so, a net movement of molecules must occur in an effort to balance the concentration gradient.
- Water will move from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration (in other words, an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration). The solute concentration in B is lower than the solute concentration in A.
- Which of the following is true of diffusion?
- Diffusion of particles along the concentration gradient will occur until particles are equally distributed in all areas of the solution.
- During diffusion, particles will move along the concentration gradient from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration in an effort to reach equilibrium (when the molecules are even throughout a space). This process does not require any energy.
- Diffusion of particles along the concentration gradient will occur until particles are equally distributed in all areas of the solution.
- Which of the following molecules crosses through a semipermeable membrane during the process of osmosis?
- Water
- Osmosis is the net movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
- Water
- The diagram below represents a plant cell and its changes as a result of two laboratory procedures, A and B. What type of solution was the cell placed in during procedure A?
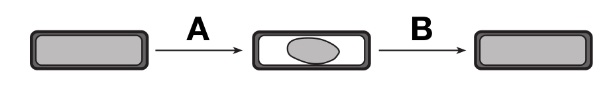
- A hypertonic solution – During procedure A, the cell shrunk. This means the cell must have been placed in a solution containing a lower water concentration and higher solute concentration. Water moved from inside the cell to out of it, causing the cell to shrink.
- A hypotonic solution is a solution that contains a higher water concentration and a lower solute concentration compared to another solution. If this was the case for the solution in the problem, water would have moved from outside the cell to inside of it, causing the cell to swell.
- An isotonic solution is a solution that contains an equal concentration of water and solute compared to another solution. If this was the case for the solution in the problem, there would have been no net water movement into or out of the cell.
Recent Comments