Digestion in Intestines:
- True statements about villi
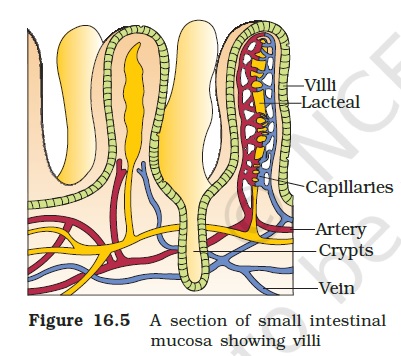
- Villi are finger-like projections found on the inner lining of the small intestine.
- Villi increase the surface area for absorption of nutrients.
- Villi are richly supplied with blood vessels. They help in the absorption of food by increasing the available surface area.
- Villi are finger-like projections found on the inner lining of the small intestine.
- Which pancreatic enzyme digests protein in the alimentary canal?
- Trypsin is the pancreatic enzyme that digests protein.
- Which of the following enzymes are found in the pancreatic juice?
- Trypsin and Lipase
- Trypsin and lipase are the two main enzymes found in pancreatic juice secreted from the pancreas into the small intestine.
- Trypsin is the pancreatic enzyme that digests protein.
- Trypsin works best in slightly alkaline conditions.
- Trypsin and Lipase
- Why should the acidic nature of food from the stomach be changed in the small intestine?
- To activate the pancreatic enzymes, it require an alkaline environment to function and therefore, the acidic nature of food entering into the small intestine from the stomach needs to be changed.
- What happens during emulsification of fat?
- Large fat globules are broken into tiny fat droplets by bile salts.
- During emulsification, fat globules are broken into tiny fat droplets by bile salts, which increases the surface area for digestive enzymes(lipase) to act upon.
- Emulsification of fat is done by bile salts. This process is not affected much by the acidic or basic nature of food.
- Emulsification breaks fat globules into tiny droplets, providing more surface area for pancreatic lipase to act.
- Large fat globules are broken into tiny fat droplets by bile salts.
- What are the end products of fat digestion?
- Fatty acids and glycerol are the end products of fat digestion.
- Fat digestion is performed in the small intestine
- Fatty acids and glycerol are the end products of fat digestion.
- Which secretion changes the nature of food from acidic to alkaline in the small intestine?
- Bile juice
- Bile juice is alkaline and, therefore, changes the acidic nature of food arriving in the small intestine from the stomach.
- The liver secretes bile juice that helps in digestion of fats
- Bile juice
- Herbivores have a longer small intestine as compared to carnivores because they need to digest cellulose, which takes more time than digestion of meat.
- A horse is an herbivore, so its diet is mostly made up of plants. Therefore, it will have a long small intestine to carry out digestion of cellulose

- Amino acids are the end products of protein digestion
- HCl helps in protein digestion by activating the protein-digesting enzyme, pepsin, in the stomach.
- Which component of food is normally absorbed in the large intestine as well as the small intestine?
- Absorption of water takes place in the large intestine as well as the small intestine.
- Carbohydrates are largely absorbed in the small intestine after being broken down into simple sugars.
- Proteins are largely absorbed in the small intestine after being broken down into amino acids.
- Fats are largely absorbed in the small intestine after being broken down into fatty acids and glycerol.
- Absorption of water takes place in the large intestine as well as the small intestine.
Human digestion:
- The digestion of which food component begins in the stomach?
- Protein digestion starts in the stomach.
- Digestion of fats occurs mainly in the small intestine. The mouth and stomach lack significant fat-digesting enzymes.
- Digestion of starch by salivary amylase begins in the mouth.
- Protein digestion starts in the stomach.
- Which gland in the human body is responsible for initial digestion of starch?
- Saliva secreted by these glands contains salivary amylase, which initiates the digestion of starch in the mouth.
- The pancreas aid in later digestion in the small intestine.
- The liver secretes bile juice that helps in digestion of fats
- Gastric glands secrete pepsin that digests protein
- Salivary amylase in saliva works in near-neutral conditions found in the mouth.
- Saliva secreted by these glands contains salivary amylase, which initiates the digestion of starch in the mouth.
- Pepsin gets activated only in the highly acidic environment created by HCl secretion in the stomach
- Pepsin digests protein in the stomach. It is not a pancreatic enzyme.
- Gastric glands secrete pepsin that digests protein.
- What is the main function of the mucus in the stomach lining?
- It protects the stomach wall from the corrosive effects of HCl
- Mucus prevents corrosion from HCl by providing a protective inner lining to the stomach.
- It protects the stomach wall from the corrosive effects of HCl
- Which of the following is NOT a component of gastric juice?
- Trypsin is secreted by the pancreas into the small intestine, not the stomach.
- HCl is secreted by gastric glands in the stomach.
- Mucus is secreted by gastric glands in the stomach.
- Pepsin is secreted by gastric glands in the stomach.
- Trypsin works best in slightly alkaline conditions.
- Trypsin is secreted by the pancreas into the small intestine, not the stomach.
- The function of HCl in the stomach
- Activation of pepsin
- HCl helps in protein digestion by activating the protein-digesting enzyme, pepsin, in the stomach.
- Elimination of harmful bacteria that enter the stomach with food.
- HCl creates a highly acidic environment that kills most harmful microorganisms like bacteria that might enter the stomach.
- Activation of pepsin
- The digestion of which food component begins in the stomach?
- Protein digestion starts in the stomach.
- Digestion of starch by salivary amylase begins in the mouth.
- Digestion of fats occurs mainly in the small intestine. The mouth and stomach lack significant fat-digesting enzymes.
- Protein digestion starts in the stomach.
Transportation in human beings:
- Why do mammals and birds have separate right and left chambers in their heart?
- To prevent the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood inside the heart
- Separation of the heart into right and left chambers creates a physical barrier that prevents the oxygenated blood from mixing with the deoxygenated blood.
- To meet their high energy demands
- Mammals need high energy and oxygen is needed by cells to generate this energy. Separation of the heart into right and left chambers ensures that the oxygen content of the blood to be pumped remains high.
- To maintain temperature
- Maintenance of body temperature requires energy which is generated when oxygen-rich blood is pumped to the cells.
- To prevent the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood inside the heart
- In higher classes of animals like mammals and birds, oxygenated blood is completely separated from deoxygenated blood inside the heart. This is not true in lower animals like fishes and reptiles. Why does oxygenated blood need to be prevented from mixing with deoxygenated blood inside the hearts of birds and mammals?
- Mammals need to maintain their body temperature
- Maintenance of body temperature requires energy and energy production further depends on the supply of oxygen. Separation of oxygenated blood from the deoxygenated blood in the heart ensures that the blood which is pumped from the heart is rich in oxygen.
- Mammals need to maintain their body temperature
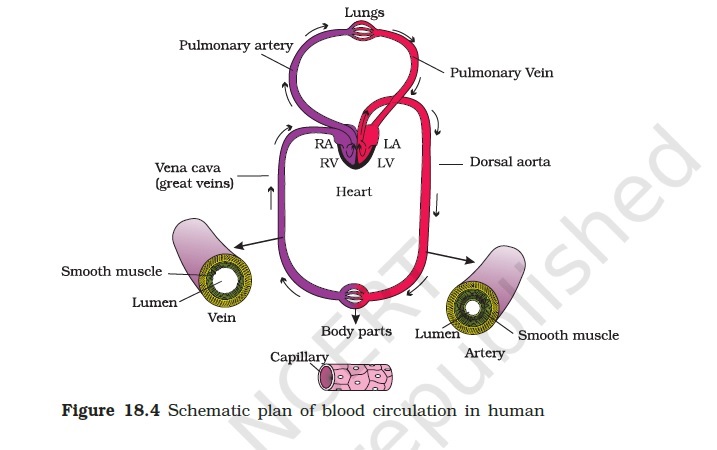
- the chambers of the heart with the thickest walls
- Left ventricle
- The left ventricle is the chamber with the thickest muscular walls. This allows it to contract with enough force to pump blood to different parts of the body.
- Right ventricle
- The right ventricle has thick walls that enable it pump blood from the heart to the lungs.
- Left ventricle
- The human heart is divided into four chambers that help in blood circulation between the heart, lungs and the body. The chambers also prevent deoxygenated blood from mixing with oxygenated blood while pumping. Which chamber of the heart pumps the deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs?
- Right ventricle
- The right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
- Right ventricle
- Which chamber of the heart contracts to pump oxygenated blood from the heart to different parts of the body?
- Left ventricle
- The left ventricle contracts to pump oxygenated blood from the heart to different parts of the body.
- Left ventricle
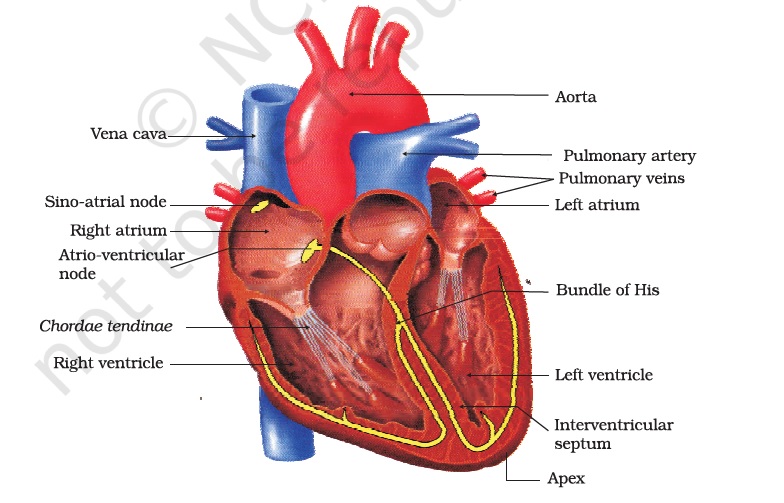
- The human heart works continuously to supply oxygenated blood to all organs. The four chambers of the heart, the blood vessels and the lungs work together to achieve this. Which chamber of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs?
- Left atrium
- The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through pulmonary veins.
- Left atrium
Blood vessels and their maintenance:
- Which of the following components of blood is primarily involved in clotting of blood?
- Platelets
- Platelets are primarily involved in blood clot formation. The platelets, along with some other clotting factors, plug the leaks in the blood vessels at the site of injury.
- Platelets
- Which of the following problems is likely to be caused by platelet deficiency?
- Difficulty in blood clot formation at the site of injury
- Since platelets are primarily involved in the process of blood clot formation at the site of injury, a deficiency of platelets will lead to difficulty in this process.
- Difficulty in blood clot formation at the site of injury
- The spaces between the cells of the tissues are filled with a clear fluid called tissue fluid. The tissue fluid is referred to as lymph once it enters circulation inside the lymph vessels. The lymph carries digested and absorbed fat from the intestine and helps in draining out excess fluid from intercellular spaces. Choose the statements that correctly describe the nature of lymph.
- Lymph contains less proteins than the blood plasma.
- A very small fraction of proteins found in the blood plasma escape from the walls of blood capillaries. So, lymph contains less proteins than blood plasma.
- Lymph is transferred back to the blood through the lymphatic vessels.
- The lymphatic vessels eventually join the veins where they transfer lymph back to the blood.
- Lymph originates from blood.
- Lymph is formed as a result of movement of some amount of plasma, proteins, and cells from blood through the walls of capillaries.
- Lymph contains less proteins than the blood plasma.
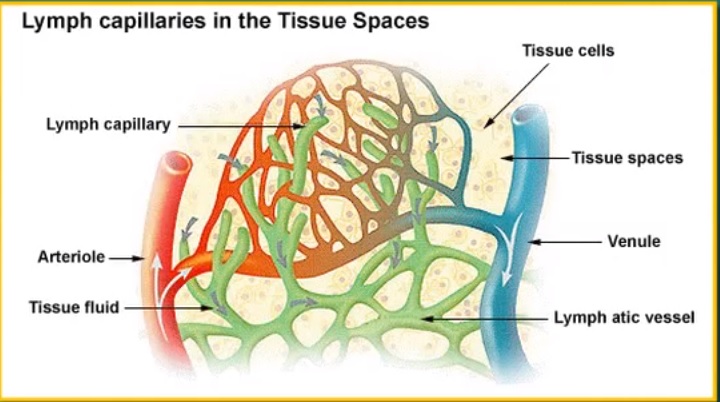
- When the blood flowing under pressure from the heart reaches the capillaries, some amount of plasma, proteins and blood cells get filtered out from the thin capillary walls into the intercellular spaces. This filtered out fluid is similar to the plasma except that it is colorless and contains less protein. Choose correct statements about this fluid.
- This fluid is called tissue fluid or lymph.
- The fluid that gets filtered out from the capillaries is called tissue fluid or lymph.
- This fluid is transferred back to the blood via lymph vessels.
- The tissue fluid that gets filtered out from the blood into the intercellular spaces is collected by the lymph capillaries. Many lymph capillaries join to form lymph vessels that finally join the veins.
- This fluid carries digested and absorbed fat from the intestine.
- Digested and absorbed fat from the intestine is carried by the lymph.
- This fluid is called tissue fluid or lymph.
- Identify the statements that correctly differentiate arteries from veins.
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart, whereas veins bring blood to the heart.
- Arteries carry blood from the heart to the rest of the body, whereas veins carry blood back to the heart from the rest of the body.
- Veins have valves whereas arteries do not have valves.
- Veins have valves to prevent back flow of the blood whereas arteries do not.
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart, whereas veins bring blood to the heart.
- What is the main function of blood capillaries?
- To facilitate the exchange of materials between the blood and the cells of the body.
- Capillaries facilitate the exchange of materials between the blood and the cells of the body because capillaries are very fine and their walls are only one cell thick.
- To facilitate the exchange of materials between the blood and the cells of the body.
- Identify the characteristics of blood vessels that are true only for veins.
- Presence of valves
- Veins have valves to prevent back flow of blood. Arteries don’t require valves because the high pressure within them prevents back flow of blood.
- Blood flows towards the heart
- Blood inside veins flows towards the heart, whereas blood in arteries flows away from the heart.
- Presence of valves
- Which of the following processes are facilitated because blood capillaries happen to be very fine and their walls are only one cell thick?
- Exchange of gases in alveoli.
- Alveoli are richly supplied with blood capillaries that facilitate the diffusion and exchange of gases through their thin walls.
- Penetration of capillary network deep inside the tissues.
- Capillaries are very fine structures. They can penetrate deep inside tissues, where they facilitate the exchange of materials between the blood and surrounding cells.
- The diffusion of oxygen from blood to the surrounding cells.
- The rate of diffusion of oxygen from blood to the surrounding cells depends on the thickness of the walls of the blood capillaries. Because the walls of the blood capillaries are only one cell thick, the rate of diffusion becomes high.
- Exchange of gases in alveoli.
Neurons:
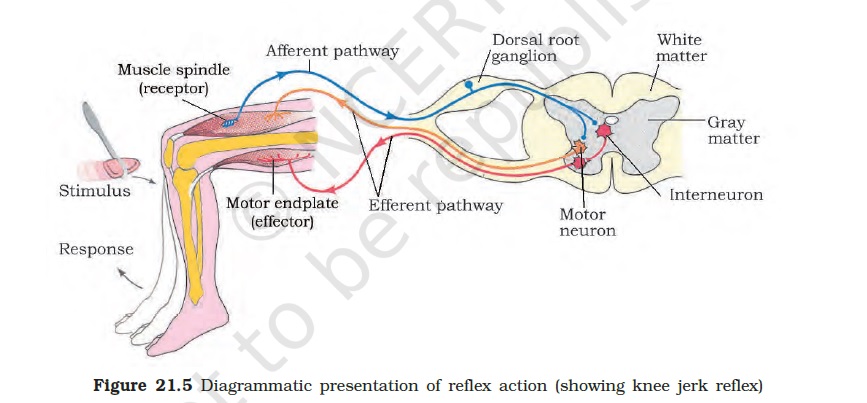
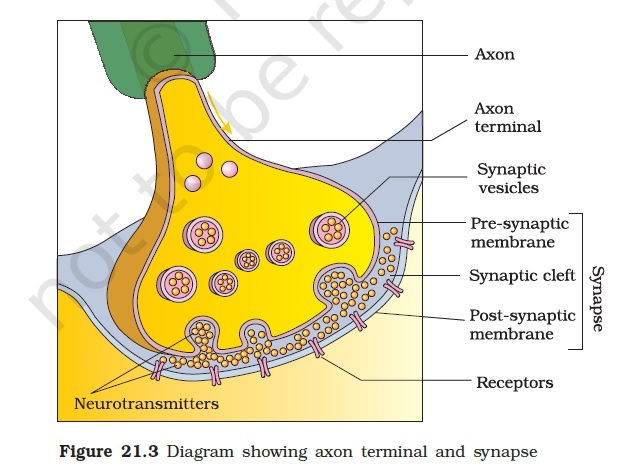
- Chemicals called neurotransmitters transfer information between two neurons separated by a gap. These chemicals pass the information from axon terminal of the first neuron to the dendritic tip of another neuron. What is this area of contact of two neurons called?
- Synapse
- The area of contact of two neurons is called a synapse.
- Synapse
- A neuron transfers information by releasing chemicals called neurotransmitters. These chemicals are released from axon terminal in an area called synapse.
- Choose all correct statements about synapse.
- Chemicals help in passing information through the synapse.
- Chemicals called neurotransmitters convey information through the synapse.
- Synapse helps in delivering the message from the neuron to the muscles.
- Message from the neuron is delivered to the muscles through release of chemicals at the neuromuscular junction. The neuromuscular junction is the synapse between a neuron and a muscle cell.
- An electrical signal is converted into a chemical signal at the synapse.
- An electrical signal is converted into a chemical signal in order to transfer information through the gap at the synapse.
- Chemicals help in passing information through the synapse.
- Choose all correct statements about synapse.
- Chemicals called neurotransmitters transfer information between two neurons separated by a gap. These chemicals pass the information from axon terminal of the first neuron to the dendritic tip of another neuron. What is this area of contact of two neurons called?
- Synapse
- The area of contact of two neurons is called a synapse.
- Synapse
- Messages from the brain to the muscles are delivered through the neurons. The axon terminal of neurons release chemicals near the muscle cells and these chemicals finally cause action in the muscle. What is the area of contact between the neuron and the muscle cell called?
- Neuromuscular junction
- Neuromuscular junction refers to the synapse between a neuron and a muscle cell. It is in here that chemicals are released by neurons.
- Neuromuscular junction
- Information through neurons can travel as fast as 400 km/hr. This is because the information inside a neuron travels in the form of an electrical impulse. Which of these will happen to a neuron if its axon fails to function?
- It won’t send impulse to the neighboring neuron.
- Axon carries the electrical impulse generated in the cell body to the neighboring neuron. Damage to axon will inhibit this process.
- It won’t send impulse to the neighboring neuron.
- What is the role of the dendrites of a neuron at the synapse?
- Dendrites receive information at the synapse.
- Dendrites receive information through the chemicals released from the axon terminal at the synapse.
- Chemicals are released by axon terminals at the synapse.
- Dendrites receive information at the synapse.
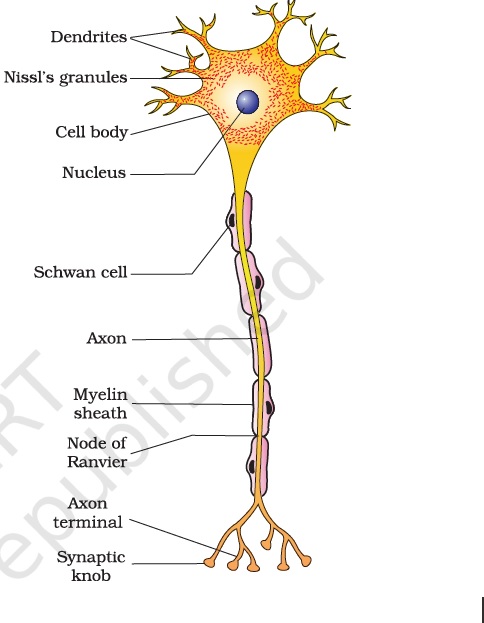
- Which part of a neuron generates an electrical impulse?
- Cell body
- Cell body is a part of neuron and contains the nucleus.
- An electrical impulse is generated in the cell body.
- Axons carry the electrical impulse from the cell body to the axon terminal.
- Dendrites carry information towards the cell body whereas an axon carries information away from the cell body.
- Cell body
Functions of brain:
- A drunk person often loses balance as he walks. This happens because alcohol also affects part of the brain that controls body balance. Which part of the brain controls body balance and posture?
- Cerebellum
- Cerebellum regulates posture and body balance.
- Cerebellum
- Activities, like riding a bicycle, drawing sketches and playing sports require controlled and precise movements of body parts. Which part of the brain controls such precise body movements?
- Cerebellum
- Cerebellum controls precise body movements, posture, and balance.
- Cerebellum
- All the information received from the external environment is processed in the central nervous system which is the center for our thoughts and decisions. Which of the following are components of the central nervous system?
- Brain
- Brain is a component of the central nervous system and the center for all our thoughts.
- Spinal cord
- It is present inside the vertebral column is a component of the central nervous system. Spinal cord controls all our reflex actions.
- Brain
- To answer a question like this one you read, think, recall, and then give a response. You are able to understand what is being asked because of the ability of your brain to think. Which part of your brain is currently performing the function of thinking as you answer this question?
- Forebrain
- Forebrain is the main thinking part of the brain.
- Forebrain
- Medulla is located in your hind brain and is responsible for making you vomit. But, it also has some other important functions. Which of the following body functions are controlled by medulla oblongata?
- Breathing
- Breathing is a basic life function regulated by medulla.
- Blood Pressure
- Blood flow and pressure is a basic life function controlled by medulla.
- Heart rate
- Beating of heart is a basic life function controlled by medulla.
- Breathing
- The peripheral nervous system carries information of touch, smell, sound etc. to the central nervous system where this information is processed to derive meaning and make a decision. Which of the following are components of the peripheral nervous system?
- Spinal nerves
- Spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord are a component of the peripheral nervous system. They carry information to and from the spinal cord.
- Cranial nerves
- Cranial nerves arising from the brain are a component of the peripheral nervous system. They carry information to and from the brain.
- Spinal nerves
- Identify the color of any three objects around you. Now think about the process through which you were able to do this. Obviously, the information about the objects was collected by your eyes and passed to your brain where it was processed. Which part of the brain receives and processes the information from the eyes?
- Forebrain
- Different parts of the forebrain receive and process the information from the eyes.
- Forebrain
- While your mind is analyzing this question, your heart is beating and your stomach is digesting the food you ate. You are not even aware of such functions of your stomach or heart. Which part of the brain performs these involuntary life-sustaining activities?
- Medulla Oblongata
- The basic life-sustaining involuntary activities like breathing and digestion are regulated by the medulla.
- Medulla Oblongata
Parts of the human eye:
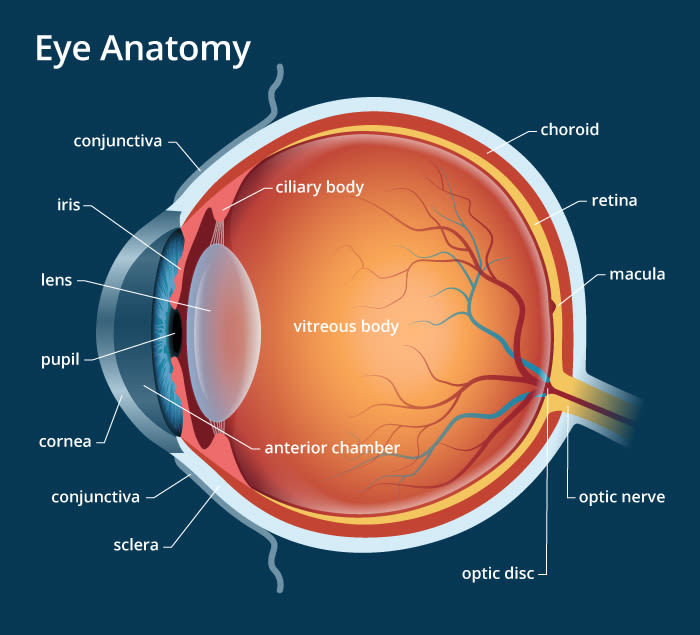
- Which of the following statements are true about the cornea?
- It’s a thin membrane that forms a transparent bulge on the front surface of the eye.
- It’s the outermost layer of the eye. No, please don’t touch it.
- Most of the refraction of the incoming light rays occurs at the cornea.
- Although it might seem that most of the refraction occurs inside the lens, it actually occurs at the cornea.
- It’s a thin membrane that forms a transparent bulge on the front surface of the eye.
- Which of the following statements are true about the retina?
- It’s a thin membrane located at the back of the eye.
- It acts as the screen on which images are formed.
- The retina consists of a large number of light-sensitive cells.
- There are two kinds of light sensitive cells on the retina, the rod and the cone cells.
- The light-sensitive cells on the retina get activated upon illumination and generate electrical signals.
- The rod and the cone cells respond to incoming light and convert the visual information into electrical signals.
- It’s a thin membrane located at the back of the eye.
- Which of the following statements are true about the iris?
- It’s a muscular diaphragm. It’s a circular muscular structure that also determines the colour of your eyes!
- It controls the size of the opening through which light falls on the lens.
- It has a circular opening in the middle. By contracting or relaxing, the iris controls the size of the opening.
- Which of the following statements are true about the optic nerve?
- It’s attached to the back of the eyeball.
- Like a tail.
- It sends the electrical signals generated by the retina to the brain.
- The optic nerve connects the retina to the visual cortex in the brain.
- It’s attached to the back of the eyeball.
- Which of the following statements are true about the ciliary muscles?
- They are directly attached to the lens.
- Ciliary muscles consist of a large number of fibres that are directly connected to the lens.
- They contract or relax to control the shape of the lens.
- The muscular fibres in the ciliary muscles can contract or relax to make the lens thicker or thinner, as required for focussing
- They are directly attached to the lens.
- Which of the following parts is a circular opening that regulates the amount of light entering the eye?
- The pupil is a circular opening right in front of the lens through which light enters the eye. It dilates to let more light in and shrinks to reduce the amount of light entering the eye.
- Which of the following parts is a transparent, crystalline structure that provides adjustment to the focal length of the eye?
- The lens is transparent and crystalline. It can become thinner or thicker to adjust its focal length depending on whether the object is distant or nearby.
- Which of the following parts is a thin membrane that forms a transparent bulge in front of the eyeball, where most of the refraction of incoming light occurs?
- The cornea is a thin, transparent membrane that forms a bulge on the front of the eyeball. It’s also responsible for most of the refraction of incoming light before it even hits the lens.
- Which of the following parts is a delicate membrane dotted with light-sensitive cells on which the images form?
- The retina lines up the inside of the eyeball opposite to the lens and is dotted with hundreds of millions of rod and cone cells that are activated by incident light
- Which of the following parts is a muscular diaphragm located in front of the lens with a circular opening at the centre?
- Iris It’s a circular muscular structure that also determines the colour of your eyes
- Which of the following parts transmits electrical signals from the eye to the brain?
- Optic nerve – Located at the back of the eye, it transmits electrical signals from the retina to the brain.
- Which of the following parts contracts or relaxes to control the shape of the lens?
- The group of ciliary muscles –
- The ciliary muscles are connected to the lens through numerous fibres that contract or relax to make the lens thinner or thicker as required. The mechanism is rather complex.
- The group of ciliary muscles –
- Which of the following statements are true about the pupil?
- It’s the opening through which light falls on the lens.
- The pupil is not a physical part. It’s actually just the hole that the iris forms in front of the lens.
- It controls the amount of light entering the eye.
- When the pupil dilates, more light enters the eye. When the pupil shrinks, less light enters the eye.
- It’s the opening through which light falls on the lens.
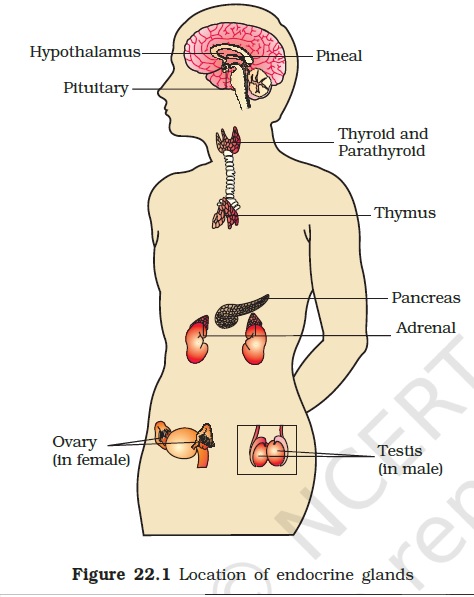
Hormones :
- Imagine a deer being chased by a cheetah in the wild! In such emergency situations, a hormone called adrenaline is secreted in the body which prepares animals to fight or run away. Which of the following effects are produced by secretion of this hormone in the body?
- Increased heart rate
- Heart rate is increased to pump more of oxygen and glucose rich blood to required organs like skeletal muscles.
- Increased breathing rate
- Adrenaline increases the breathing rate so that more oxygen is available for the body.
- Increased blood supply to skeletal muscles
- Since blood carries oxygen and glucose, increased blood supply means more oxygen and glucose available for skeletal muscles.
- Increased heart rate
- When a person encounters an emergency situation (e.g. being chased by a mad dog) his heart starts beating faster, his breathing rate increases and his muscles become more capable due to the increased blood supply in them. Which hormone produces such effects that prepare animals to fight or escape from emergency situations?
- Adrenaline
- Adrenaline produces effects that prepare the body for emergency situations. It is for this reason that adrenaline is also called “emergency hormone” or “fight or flight hormone.”
- Stress response is regulated by nervous system and adrenaline hormone.
- Adrenaline
- Our pancreas produce insulin. People with diabetes either do not produce enough insulin or their body cannot effectively utilize the insulin produced. What is the role of insulin in the body?
- Insulin lowers the level of sugar in the blood.
- Insulin lowers the level of sugar (glucose) in the blood by removing glucose from the blood and depositing it in the liver.
- Blood sugar level is regulated by two hormones, insulin and glucagon.
- Glucagon(hyperglycemic hormone) acts mainly on the liver cells (hepatocytes) by glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis.
- Insulin lowers the level of sugar in the blood.
- With the highest number of diabetes patients, India is called the diabetes capital of the world. Diabetes occurs when there is a deficiency of insulin in the body or when the body is not able to use the insulin it produces. Which of the following is a function of insulin in the body?
- Insulin regulates level of sugar in the blood.
- Insulin regulates level of sugar in the blood by removing excess glucose from the blood and depositing it in the liver.
- Insulin acts mainly on hepatocytes and adipocytes and enhances cellular glucose uptake and utilisation.
- Insulin regulates level of sugar in the blood.
- The best balance for growth is provided by controlled metabolism of various food components like proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Which hormone regulates such metabolism in the body?
- Thyroxine
- Thyroxine regulates the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and fats in the body.
- Thyroxine
- Today, the salt sold by most companies has iodine added in it and is labeled as “iodized salt”. The aim of supplying iodized salt is to prevent goiter and other iodine deficiency disorders by adding iodine to our diet. Why is iodine needed in the body?
- Iodine helps in the synthesis of thyroxine.
- Iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroxine in the human body.
- Iodine helps in the synthesis of thyroxine.
- Growth and development of the human body are regulated by the growth hormone. Its deficiency leads to dwarfism whereas its over secretion makes people abnormally tall. Which gland secretes this hormone?
- Pituitary gland
- Pituitary gland secretes growth hormone.
- Pituitary gland
- Since the synthesis of thyroxine hormone by thyroid gland requires iodine, the deficiency of iodine in the diet leads to a deficiency of thyroxine hormone in the body. Which of the following disorders is caused by a deficiency of thyroxine hormone?
- Goiter is caused by a deficiency of thyroxine hormone.
- The growth of facial hairs and deepening of voice are two visible signs of puberty in boys. In girls, development of breasts is a visible sign of puberty. Which of the following hormones are responsible for such changes during puberty?
- Testosterone
- Testosterone causes puberty related changes in boys.
- Oestrogen causes puberty related changes in girls.
- Testosterone
- An investigation by the New York Times in 1985 found 40 million Indians to be iodine deficient. Majority of these people lived in the Himalayan region where iodine levels were very low in the soil and water. The problem was solved by supplying “iodized salts”.Why is iodine essential for our body?
- Iodine helps in synthesis of thyroxine.
- Synthesis of thyroxine hormone in the thyroid gland requires iodine.
- Iodine helps in synthesis of thyroxine.
- Iodine is required in the diet because it is a component of an important hormone called thyroxine. The “iodized salts” that we eat help in the production of thyroxine by thyroid glands. Which of the following is a function of thyroxin?
- Thyroxine regulates carbohydrate metabolism.
- Thyroxine regulates protein metabolism.
- Robert Wadlow was the world’s tallest man who reached a height of 8 feet 11 inches before his death at the age of 22 years. His abnormal height was due to oversecretion of the growth hormone. Which gland in the human body secretes this hormone?
- Pituitary gland secretes growth hormone.
- Hormones are effective in very small quantities and their secretion from endocrine glands is precisely regulated. Both deficiency and over secretion of hormones lead to disorders. Which of the following disorders is caused by over secretion of a hormone?
- Gigantism is caused by over secretion of growth hormone.
- Puberty is the period during which a child’s body develops and becomes capable of sexual reproduction. Different changes start taking place in the bodies of boys and girls during puberty. Which of the following hormones are responsible for changes associated with puberty?
- Testosterone brings puberty related changes in males.
- Oestrogen brings puberty related changes in the female body.

Recent Comments