Democratic administration needs leadership at different levels. The school administration must possess the qualities of leadership so that others may also follow. One should inspire, direct, guide and lead the staff, the students, the parents and the community as well.
Leadership Models:
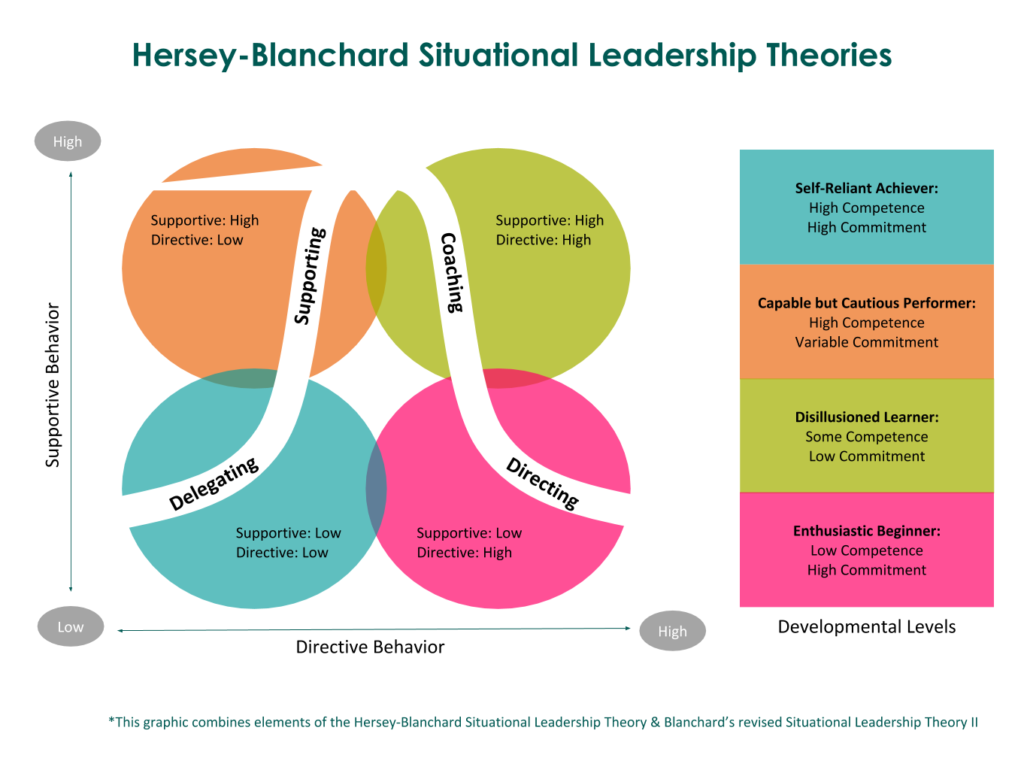
Situational leadership theory is a theory of leadership that talk about leadership with the focus on the readiness and willingness of employees. The four levels of readiness of employees are depicted have been identified as
- Unable and unwilling – leader is required to give clear and specific directions
- Unable and willing – leader should inspire and motivate the employees to buy
in to his desire - Able and unwilling – use of supportive and participative style is necessary
- Able and willing – not much action is required
Leadership style and classified into two types
- Task centred leadership style (Directive behaviour)
- Relationship oriented behaviour (Supportive behaviour)

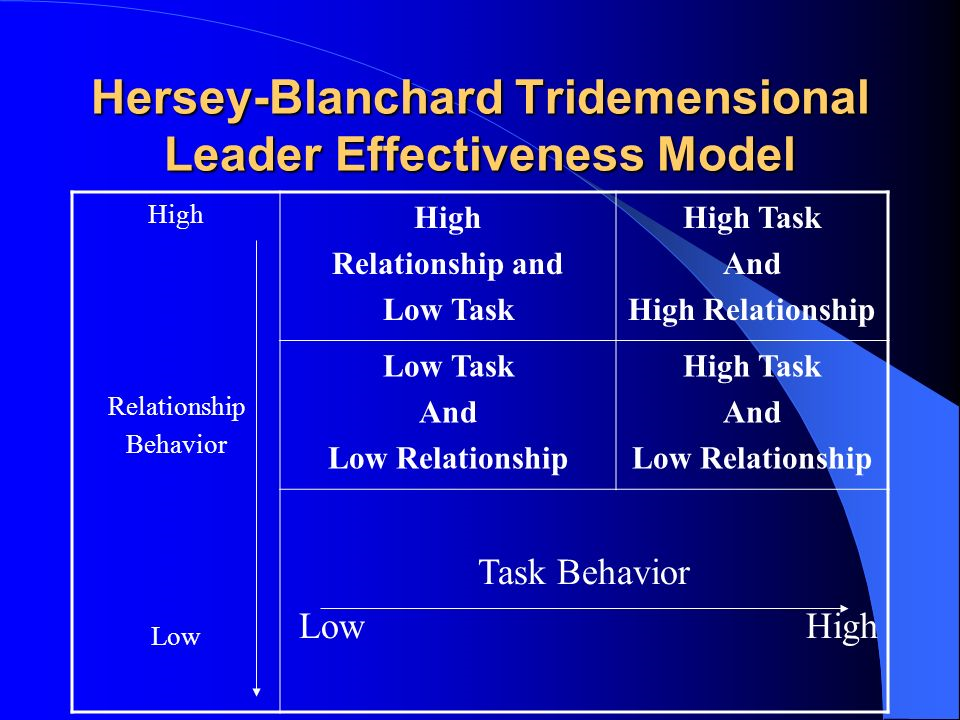
- List-I (Level of Task and Relationship Orientation) List-II (Name of the Leadership Style) – (Characteristic of the situation) – Power basis
- High task low relationship – Directive style relationship – Followers are high in three Cs (Commitment, Competence and Cohesiveness) – Coercive power
- Low task high relationship – Participating style – Followers are high in any one of the three Cs – Information power
- High task high relationship – Supportive style – Low in any one of the three Cs- Reward power
- Low task low relationship – Delegating style relationship – Legitimate power/Expert power
- List-1 (Leadershipstyle)List-II(Powerbasis)
- Telling style – Coercive power – Leader provides specific guidance by establishing work schedules and rules
- Selling style – Reference power – High task and low relationship – leader consults subordinates thereby permitting them to participate in decision making
- Participating style – Legitimate power – low task and high relationship – leader establishes good relation with subordinates thereby permitting them to participate in decision making
- Delegating style – Expert power – Leader set challenging goals and seeks improvement in performance
- Blake Mouton Managerial grid theories of leadership. It explains how leaders try to accomplish the goals of an organization through their two types of orientations i.e. concern for production and concern for people
- Set-I (Styles of leadership) – Set-II (Characteristics)
- Impoverished leadership – Laissez-faire-minimal concern for both the workers and the task
- Country club leadership – Focusses on creating safe, comfortable working environment, minimal conflict
- Task-oriented leadership – Autocratic-workers have to complete the task, nothing else
- Team leadership – Staff/workers closely involved in decision-making and feel valued
- Middle of the road leadership – Compromises made to achieve acceptable performance
- Set-I (Styles of leadership) – Set-II (Characteristics)
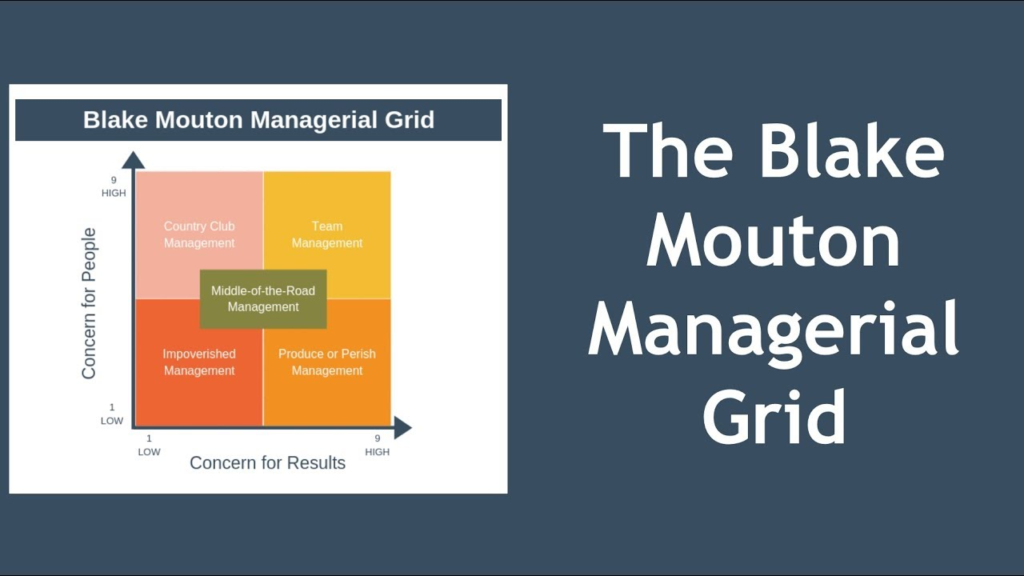
Concern for production:
- Policy decisions Product development Process issues Sales volume Production targets Work loads
Concern for people:
- Good working conditions Fair and equitable salary structures Good relations Trust building Commitment enhancing
Trait approach:
- Trait theories of leadership focus on personal qualities and characteristics
- The main characteristics which are related with leader-member exchange theory :
- Views leadership as a process.
- Focuses on the vertical dyadic relationship.
- Explains the effects of leader ship on members, teams and organisation.
- Points out what strengthens and weakens the leadership dynamics.
- For promoting effective leadership Transformational theory has a greater potential
these are those leaders who are able to inspire
their followers to rise above self interest in the favour of the organizational goal.
They usually have a profound, long lasting and extraordinary effect on their
followers. Some characteristics of transformational leaders are
- Idealized influence – provides the vision and goals, and the zeal to
- work towards the goals.
- Inspirational motivation – properly communicates the expectations and
- inspires to exceed expectations.
- Intellectual stimulation – promotes intelligence, rationality and
- problem solving.
- Individualised consideration – treats the followers as individuals and
- recognises the needs of different people are different.
- Transactional leadership – these leaders motivate or inspire their followers towards the direction of established goals through providing clear goals and task requirements. These kinds of leader have some specific characteristics
- Contingency rewards –exchange of rewards for good performance and effort.
- Management by exception – observes for deviation from set rule and interferes to take corrective action.
- Laissez-Faire – minimal concern for both the workers and the task
- The sets of statements gives acceptable difference between transactional and transformational leadership styles for strengthening the school system
- In transactional leadership style, the leader goes with his/her own vision while in transformational style, the leader creates vision in others.
- Transactional style leader monitors while in the transformational style leader inspires.
- In transactional leadership style, the leaders personal traits are important while in transformational style, inter relationships are important.
- The transactional leader monitors while the transformational leader guides.
- Fiedler’s contingency model of leadership:
This theory attempts to predict how style of leader, task structure, leader-member relations and position power act in a combination to achieve productive outcome in the organization.
Assumptions of this model:
Leadership styles are fixed
Relationship based leadership style (people – oriented)
Task based leadership style (Production – oriented)
To arrive at leadership style, LPC (least preferred coworkers) questionnaire is used. LPC is the person with whom leader finds difficulty to cooperate and MPC (Most preferred coworkers) are those who are easy to cooperate with. Leaders are asked to rate both MPC and LPC.
Dynamics of Leadership:
- According to contingency or situational the decision-making by the leaders should be done according to situations rather than according to principles.
- Thus, there is no such single formula or principle which can be applicable in case of all the situations.
- This is because of the fact that the nature of environmental factors in an organisation changes every now and then. These environmental factors can be both internal as well as external factors.
- The internal factors are those which exist within an organisation such as policies, objectives, structure of the organisation, etc.
- On the other hand, the external factors are those which prevail in the outside environment such as competition, suppliers, legal and political system, government policies, etc.
- Effective leaders acts in a dynamic environment where both internal and external factors are likely to change in a particular situation so the goals of an organisation can be attained.
The main characteristics which are related with leader-member exchange theory:
- Views leadership as a process.
- Focuses on the vertical dyadic relationship.
- Explains the effects of leader ship on members, teams and organisation.
- Points out what strengthens and weakens the leadership dynamics.
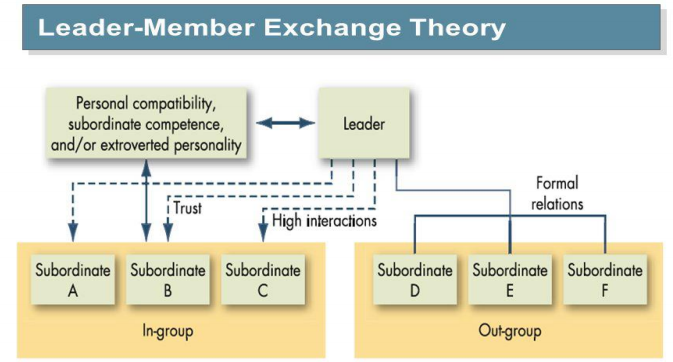
Leader –member relations: The degree to which there is mutual trust, respect, confidence and understanding between leader and followers. L-M relations are categorized as good where trust, respect and mutual understanding between leader and follower are high and bad where these are less.
Task structure:
As job is a collection of different tasks. Task structure means specific tasks are required to do the job. It also means degree to which tasks are procedurized. Task structure could be high as well as low. High task structure means strict, specific set procedures are to be required to finish the job, while, low task structure means where no set procedures are required to do the job
Position power:
Power which derived from a position or vested in a position or that goes with formal structural position is called position power. The power to hire, fire and recommendations, praise etc. is called postion power. Position power can be both high as well as low.
Emotional Intelligence:
Psychological Dimension:
- The main focus of classroom management is to facilitate learning. So, it is rightly said that no learning takes place without motivation.
- Teacher motivates his students verbally and through actions (non-verbally). He also reinforces their desirable behaviours.
- In the classroom, teacher raises the level of aspiration of students. Teacher involvement in classroom management encourages student’s participation.
- The psychological dimension plays a significant role in the student’s participation and their learning. It is a criterion for an effective classroom management.

Self-awareness:
It is the ability to recognize a feeling as it happens, to accurately perform selfassessments and have self confidence. It is the keystone of emotional intelligence
Self Regulation:
Self-management or self-regulation is the ability to keep disruptive emotions and impulses in check, maintain standards of honesty and integrity, take responsibility for one’s performance, and to be comfortable with new ideas and approaches.
Self-motivation:
It is the most important internal quality of a worker. Most of us have learned to be motivated by extrinsic or external factors while a few have discovered that the deepest motivators are intrinsic. We can consciously use our values to motivate us. We can use our thoughts to motivate us, and we can even use memories of yesterday to motivate us today. However, the deepest motivator for any human being is a clear sense of meaning and purpose.
Policies, research material and a supportive environment only support an individual’s choice. In a country where teacher motivation levels are extremely low, and where the concept of critical reflection is weak, this is a significant challenge. a constantly changing environment, in terms of policy changes and government interventions; the overall notion of good practice not being sufficiently understood, or understandably varying across the diverse contexts within India and the need to constantly maintain a strong understanding of policy, which changes very fast.
Empathy:
It is the understanding of others by being aware of their needs, perspectives, feelings, concerns. It is being sensitive to what, how and why people feel and think the way they do. Being empathetic is to be able to read the emotions of other people. Empathetic people care about others and show interest in and concern for them.
This behavior of understanding, care and concern leads to Empathy- one of the important aspects of
Emotional Intelligence.
Social Skills:
Social skills are fundamental to emotional intelligence. It is the ability to develop and maintain good relationships; communicate clearly; inspire and influence others; work well in a team, and manage conflict.
The art of relationship is a skill in managing emotions in others. These are the abilities that lead one to popularity, leadership and interpersonal effectiveness.
Leadership Roles:
A teacher’s role in classroom management is more than a manager. Teacher is the leader of a class. He influences the student’s behaviour. He has to maintain classroom code and conduct which should be value based. This dimension of classroom management involves feelings, attitudes, values and affective domain of the students.

Development of teacher as a leader:
- These four roles of teacher-leaders—
- improving student achievement,
- extending their own learning,
- collaborating for school improvement, and
- supporting shared vision and values, evolve from knowledge, dedication, and experience.
- A teacher as a manager has to look into these facilities of classroom physical setting which should be conducive to learning.
- Teacher-leaders place their students’ learning as their primary goal and work within their own classrooms to improve student achievement.
- A teacher is a leader who leads colleagues toward positive change. Leadership is the ability to collaborate with others.
- A number of values and dispositions make certain individuals ideally suited for teacher leadership.
- Effective teacher leaders are open minded and respectful of others’ views. They display optimism and enthusiasm, confidence and decisiveness
- They persevere and do not permit setbacks to derail an important initiative they are pursuing. On the other hand, they are flexible and willing to try a different approach if the first effort runs into roadblocks.
- Many attributes of good teacher leaders are fundamentally the same as the attributes of good teachers:
- persuasiveness,
- open-mindedness,
- flexibility,
- confidence, and
- expertise in their fields
- To assume a leadership role, they may need expertise in curriculum planning, assessment design, data analysis.
- They may also need to develop the abilities to listen actively, facilitate meetings, keep a group discussion on track, decide on a course of action, and monitor progress.
- These four roles of teacher-leaders—
- Improving student achievement,
- extending their own learning,
- collaborating for school improvement, and
- supporting shared vision and values, evolve from knowledge, dedication, and experience.
- Continuing to learn, refine, and implement content and pedagogical knowledge, as well as knowledge about learners and learning, moves a novice teacher into the effective teachers’ category.
- When classroom teachers model best practice and develop professional expertise, they become effective teacher-leaders because they see leadership as their duty.
- Many attributes of good teacher leaders are fundamentally the same as the attributes of good teachers: persuasiveness, open-mindedness, flexibility, confidence, and expertise in their fields.
- To assume a leadership role, they may need expertise in curriculum planning, assessment design, data analysis,
- They may also need to develop the abilities to listen actively, facilitate meetings, keep a group discussion on track, decide on a course of action, and monitor progress.
- As a result students take an active role in learning.
Organisational Behavior:
Accountability refers to the process by which the education system holds itself responsible for delivering the appropriate services and for meeting the goals for educating students. Accountability can broadly be defined as the obligation of those holding power to take responsibility for their behaviours and actions.
This obligation might come out of moral, ethical need to account for one’s behavior or out of a legal requirement. It is a relational concept as it concerns the relationship between those that perform an action or deliver a service, and those on whom the action or service has an effect. accountability requires transparency so that actions can be scrutinized and further to assess the performance.
At Organizational Level:
- Human Resource Management (HRM) is a relatively new approach to manage people in any organisation.
- People are considered the key resource in this approach.
- It is concerned with the people dimension in management of an all other sub-system of an organization.
- The functional ability and efficiency of people in all subsystems of an organization heavily rely on the policies, programmes and practices of the HRM.
Organizational Principle:
- Educational guidance and supervision is an organizational behavior and must be regarded as a management responsibility at school.
- The responsibility for improvement of educational process and learning at class and school lies on the part of the educational guide, teacher and school master.
- The more educational guides rely on their expert knowledge, skills and professional abilities, the more teachers will show eagerness to accept their guidelines.
- So, respective power must be given to educational guide in proportion to one’s responsibility.
Organizational Culture: Individual Differences vs Diversity:
- Principle of individual difference – Different children develop at different rates
- Every child goes through stages of development, yet there are wide individual differences among children.
- In a classroom, teaching-learning needs to be individualized since there are individual differences among learners.
- To understand the individual difference in development it is important
- to consider both inherited characteristics as well as environmental factors and their interplay
- Children with individual differences should be taught in a school having teachers trained to use different pedagogy to meet their diverse learning needs.
- An effective teacher in a classroom, where students come from diverse backgrounds, would
- focus on their cultural knowledge to address individual differences among the group
- Individual differences can be attributed to the complex interplay between the hereditary factors and the environment.
Diversity:
- Due to scientific and technological developments, rethinking approaches to teaching and learning, explosion of knowledge, paradigm shift from teacher centered approach to learner centered approach, increased diversity in students population, changed students’ personality, increased expectations of teachers and parents from students and increasing competitions among students has changed the role of teacher.
- The complexity of diversified context (rural, urban and tribal), composition of schools (large and small) and conditions (provisioning) are major challenges to achieve equitable quality education.
- The school education system in India is observing speedy expansion coupled with increasing diversity of student population.
- Flexible and adaptable for contextualization by the states, addressing the needs of diverse schools.
Advantages of Diversity Management:
High level of Productivity:
Every organisation has its own unique structure and objectives, different strategies can be used by the company to attain high level of productivity. One of these strategies can be adopting the adopting the workplace diversity and managing the same effectively
Exchange of ideas and Team work:
In recent times teamwork is increasingly favoured by businesses and organisations as a right means of assuring better outcomes on different allocated tasks and also for the availability of products and services as per the commitment A single person taking on multiple tasks cannot perform at the same pace as a team could; therefore each team member belonging to different background brings to the table different ideas and offers a unique perspective for problem solving to effectively arrive at the best solution at the shortest possible time for the benefit of all.
Learning and growth:
Diversity at workplace is able to create an opportunity for worker’s own personal growth and development. When workers are exposed to other diverse background workers – belonging to other cultures, countries and region can help everyone to intellectually reach out and have a clear insight about the workplace. The more time spent with the diverse workforce provides an opportunity for the workers to learn and explore new things.
Cognitive process – Perception:
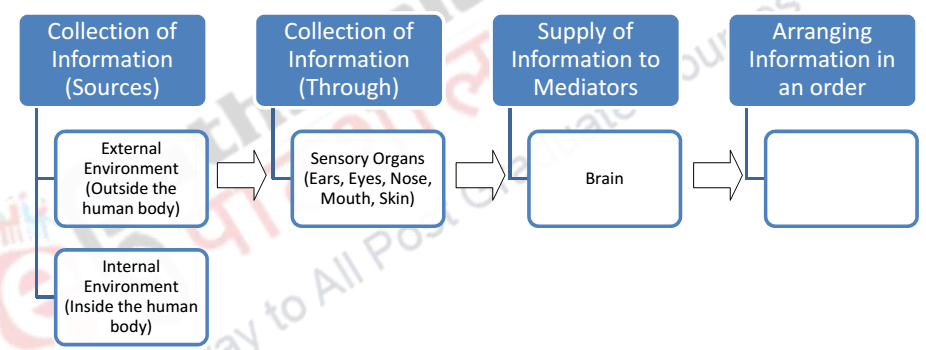
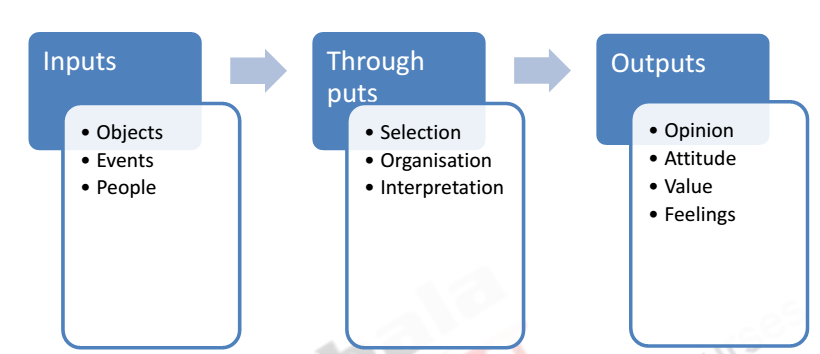
Perceptual Inputs:
It is actually receiving the stimuli from the environment.
Environment includes economic environment, political environment, socio-cultural environment,
technological environment, international environment etc. So all those things in the environment
where event occurs or contribute to the occurrence of events can be termed as perceptual inputs.
Perceptual Through puts:
It is in-fact the process of perception. Under this perceptual inputs are
converted into the perceptual outputs. In other words, during perpetual inputs the information
received is processed to obtain the output.
Selection of stimuli:
Selection of stimuli from among the various present in our surroundings is
the most important step of the perceptual process. As there are numerous stimuli prevailing in the
environment, our sensory organs are not capable enough to absorb all those stimuli. So we choose
only those towards which we get attracted to or which is related to us.
Organizational compliance:
Human resources management is interested in compliance with equal employment opportunities and observation of laws in educational sector; like employees or teachers must be oriented to the
educational institutions, supervisors must be trained, safety problems must be resolved; wages and salaries must be administered.
A wide range of activities typically associated with the day-to-day management of people as provided by laws and regulations must be performed efficiently. It is this collection of activities that
has often been referred to as the personnel function
The new importance of Human resources for effective educational functioning stems from adequately recruited, selected , supervised, inducted and adequately rewarded, provided for, properly developed, employee appraised and promoted on the job.

Code of conduct:
- A code of professional ethics is a document that outlines a set of principles, issued by a higher
authority which affect decision-making and guide the teachers to discharge their duty
towards students, parents, colleagues and community. - The standards, values, morals, principles, etc. make ethics that guide one’s decisions or actions
- Code of Conduct is essentially a set of professional ethical standards with which teachers are required to comply. It refers to the behaviour and ways of thinking of teachers in situations where a choice can affect the dignity and well being of others.
- A code of ethics can guide him towards honourable and professional behaviour and also protect its members not to go against the professional rules.
- Code of ethics and Code of conduct represent two of the most common ways of self-regulation. Code of ethics governs decision-making and code of conduct governs actions. Both codes provide direction to teachers. But, both codes regulate teachers’ behavior in different ways.
- An effective code of conduct should be written in simple language, should be positive, value-based document that must guide the teachers for appropriate behavior instead of displaying a list of rules and regulations that must be obeyed at all costs.
- This foster a culture of high standards of honesty, integrity, ethical and law-abiding behaviour among teachers.
- The main purpose is to set out the responsibility and accountability of teacher to report and investigate any reported violations of the code or unethical or unlawful behaviour.
Values in educational leadership:
- Participation: Participation by parents, teachers, community members and pupils is a key cornerstone of good school governance.
- Rule of law: Good school governance requires fair legal frameworks that are enforced impartially. It also requires promotion or protection of human rights.
- Transparency: Transparency means that decisions taken and their enforcement are done in a manner that follows rules and regulations of the school. It also means that information is freely available and directly accessible to those who will be affected by such decisions and their enforcement e.g. parents, teachers, pupils and sponsors.
- Responsiveness: Good school governance requires that school organs and processes try to serve all stakeholders, especially parents, teachers and pupils within a reasonable timeframe.
- Consensus oriented: Good school governance requires mediation of the different interests in schools to reach a broad consensus on what is in the best interest of the whole school community and how this can be achieved.
- Equity and inclusiveness:Ensuring that all members of the school community feel that they have a stake in it and do not feel excluded from the mainstream. This requires all groups, but particularly the most vulnerable, to have opportunities to improve or maintain their well-being.
- Effectiveness and efficiency: The concept of efficiency in the context of good school governance also covers the sustainable use of resources and the protection of the environment.
- Accountability: In general, an organization or an institution is accountable to those who will be affected by its decisions or actions
The Nature of groups:
- Effective management of human resource will help to improve the quality of work life.
- It will promote teamwork among employees by providing a healthy working environment.
- It can contribute for professional growth by maintaining healthy relationships among individuals, and different work groups.
- The classroom management are intimately linked to the larger concerns of
- teaching styles, motivation, interest, strategies for ensuring success, the effect of group forces and the incorporation of mental hygiene principles into daily classroom practice.
- The teacher has to involve students in daily activities of the institute like annual
functions and in co-curricular activities. - They should provide two-way communication channels. There should be regular opportunities for dialogue among students, teachers and administrators.
- Each institute should design its own programme of student involvement and this will entail, more than giving a new life to student government.
- Students should be given an opportunity to lead group discussions, to participate in departmental faculty meetings, to evaluate the academic progress of their peers and class instructional programme
- The mere knowledge of the availability of such opportunities encourages the student body to work in close collaboration with the teachers and the administrators rather than to stand against them.
- Teacher Development Groups are ideal forums to present successes and learn from failures.
- They offer networking opportunities, whether within the school, in the larger community outside, those supported by the education boards, or communities online.
Leadership and motivation:
There are two major influences that affect how individuals perform in their environment. These influences are: Type of leadership that exists and personal motivation.
While neither is scientific in nature, there is significant research that identifies some theories and general conclusions about why people perform, how they perform, and why some people display different behaviors that puts them in positions of leadership.
Motivation is a goal-oriented characteristic that helps a person achieve his objectives. It pushes an individual to work hard at achieving his or her goals. An executive must have the right leadership traits to influence motivation. However, there is no specific blueprint for motivation.
As a leader, one should keep an open perspective on human nature. Knowing different needs of subordinates will certainly make the decision-making process easier. Both an employee as well as manager must possess leadership and motivational traits. An effective leader must have a thorough knowledge of motivational factors for others. He must understand the basic needs of employees, peers and his superiors. Leadership is used as a means of motivating others.
Organizational Approaches to Stress management:
The problems of classroom management are intimately linked to the larger concerns of teaching styles, motivation, interest, strategies for ensuring success, the effect of group forces and the incorporation of mental hygiene principles into daily classroom practice.
Stressors are discovered in the physical work environment, the employee’s several life roles, personal relations, &organizational activities.
Conflicts between work and non-work responsibilities are a recurrent basis of employee stress.
Building Teamwork:
- The management should attempt to create such work environment in which there is no criteria for interpersonal fight or inter group fight.
- Such conflicts are the reasons of stress; such should be clogged from building or eliminated if they grow. Therefore such work should be established that groups & the members are mutually-operative and creative. Participants of the group should trust themselves as participants of the related family and search for sustenance from each other.
Goal Setting:
Grounded on wide amount of research it has been determined that persons perform better when they have exact & challenging aims and they gain feedback on how well they are going forward towards those aims. Goal setting can reduce stress as well as provide motivation. It will result in fewer employee annoyance, role vagueness and stress.
Improved Communication:
Many times because absence of effective communication form the bosses, the employees do not recognize what they have to perform& how they have to perform it. This ends in role ambiguity. Similarly, when two or more persons have conflicting role demands from an employee, it leads to role conflict if there is absence of proper communication. Effective communication with employees decreases the ambiguity by lessening role ambiguity & role conflict.
Redesigning jobs:
Companies should reshape the jobs in such a way as to provide employees more accountability, more expressive work, more independence, routine work, work overload or under load and role ambiguity. Job redesigning upsurges motivation, reduce the stress amongst the employees &increases “Quality of Work Life”.
Persona Wellness Programmes:
Personal wellness programmes focus on employee’s total physical & mental condition. Companies can give conveniences at their locations for physical fitness like gyms, swimming pools, tennis courts etc. as well as psychosomatic counselling.
Companies should conduct seminars or workshops to make the employee identify nature &causes of stress and the possible approaches to cut it. These workshops should help those persons who are already under stress. Moreover, a manager can influence personal wellness of subordinates with positive instances, support and by performing the indispensable ideas and methods of human resource management.
Today’s students are living in a very competitive and stressful environment. As such they may show up disturbing behavioural patterns like unusual angry outburst, excessive fighting, bullying, remaining in isolation, lacking friends, which may be indication of some serious problem in the child. In such cases students need counselling and teachers have to examine the academic and learning related problems of students in relation to their psycho-social and economic environment.
The teachers create an atmosphere in which students feel free and are motivated to learn at school as well as at home. They also assist parents to cope with issues in their everyday lives and tell them about ways and means to spare time to note disturbing behavioural patterns of the child. A sound management of school maintains the discipline and boosts the morale of pupils to behave appropriately.
Discipline plays pivotal role for smooth functioning of an institute. It also helps in providing better work culture. Schools are encouraging the teachers to use collaborative style rather than information based style when setting limitations within the classroom. The teacher with the help of leadership qualities, guides, helps and works with the students to achieve the common goals.
Leadership for Sustainable Development:
One of the major factors to ensure sustainability of programs is the availability of this regard, community participation in education cannot ensure the sustainability of schools by itself often since times communities have to rely on external funding to keep the program sustained.
Involving communities in schools is a way of reaching democracy through identifying and addressing inequities embedded in institutions and society as a whole.
In the village panchayats, as in the municipalities, a portion of the total revenue should be earmarked for Primary Education, the benefits brought by a development program will be maintained after the external interventions are stopped.

- World leaders promised to work together to meet the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) with specific targets, including that of reducing poverty by half by 2015.
- The following UN Conferences /summit adopted the program of action for sustainable development Riodejanero conference
- The Rio+ 20 Conference, 2012 or summit is also known as the UN Conference on Sustainable Development (UNCSD)
- One of the main outcomes of the Rio +20 conferences was to develop a set of Sustainable Development Goals
- SDG’s came into effect on Jan 2016
- The sustainable Development goals(SDG’s) set in 2015 by the United Nations are intended to be achieved by
- 2030
Disaster Risk Reduction and Management:
- Disaster risk reduction has been defined by UN as the “conceptual framework of elements considered with the possibilities to minimise vulnerabilities and disaster risks throughout a society, to prevent or to mitigate the adverse impacts of hazards, within the broad contexts of sustainable development.
Mainstreaming disaster risk reduction(DRR):
- Disaster risk reduction is a set of measures used to reduce the direct, indirect and tangible losses occurred due to disasters.
- This may be technical, economical or social. Mainstreaming DRR refers to the process that incorporates the concerns of disaster preparedness, prevention and mitigation into development planning as well as in the policies of post disaster recovery process.
Objectives of mainstreaming DRR:
Components of mainstreaming:
Human rights:
- Fundamental rights and directive principles are complementary to each other
- If fundamental rights are basic to political democracy, directive principles are fundamental to socioeconomic democracy in India. Without socioeconomic democracy political democracy cannot be effective.
- Civil and political rights have an instrumental value in securing government policies favourable to development and human rights
- Human rights are universal in nature
- The fundamental principle of Indian Constitution is rule of law
- The constitution of India has guaranteed to every citizen equality before law and has organised the judiciary as unfailing guardian of the rights of the people
- Fundamental rights are justiciable.
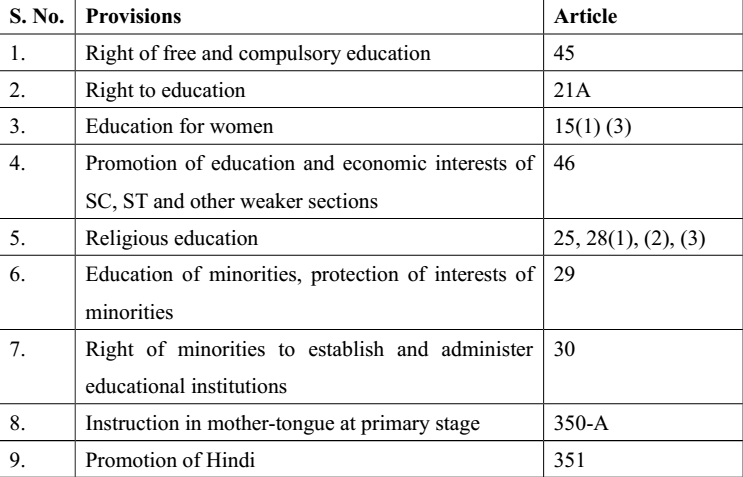
- Article 45 – Free and Compulsory Education – The state shall endeavour to provide early childhood care and education for all children until they complete the age of six years.
- Right to Education – Article 21A – The state shall provide free and compulsory education to all children of the age 6 to 14 years.
- To promote peace and tolerance in the society
- Article 25 – incorporates Provision for Religious Education.
- Article 25(1 of the constitution guarantees all the citizens a right of freedom of conscience and the right to profess, practice and propagate religion.
- Article 28 – Freedom as to attendance at religious instruction or religious worship in certain educational institutions’
- Article 29 – Protection of interests of minorities
- Article 30 – Right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions.
- Article 25 – incorporates Provision for Religious Education.
- As evidence suggests there is little correlation between civil and political rights and economic growth. Violation of such rights does not necessarily leads to economic development
- Civil and political rights have an instrumental value in securing government policies favorable to development and human rights
- Emergence of market forces has made enjoyment of human rights effective in contemporary times
- Implementation of human rights need a great deal of economic resources on the part of the state.
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan:
- Launched in 2001 Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) is one of the India’s major flagship program for universalisation of elementary education.
- Its overall goals include universal access and retention, bridging of gender and social category gaps in elementary education, and achieving significant enhancement in learning levels of children.
- Provisions of Right to Education Act are being implemented through SSA. Accordingly, norms have been revised / modified to align them with the requirement of RTE Act, 2009.
The Right to Education Act, 2009:
- The act seeks to implement the fundamental right to education for all children (including children with disabilities) between 6 to 14 years.
- The government has committed 2.3 trillion… . for five years (2010–11 to 2014–15) to implement the Act. The fund sharing pattern between the centre and the state is in the ratio of 65:35 for five years.
- The act makes it mandatory for all schools to meet certain minimum norms. They have to meet the Pupil–Teacher Ratio (PTR). All other schools require a certificate of recognition and it shall be granted if the school satisfies certain norms such as PTR, infrastructure and qualification of teachers.
Recent Comments