Organising teaching:
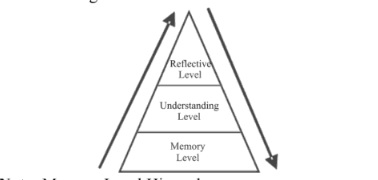
Herbart’s Model – Memory level teaching:
- To get factual information
- To train memory faculty
- To retrain the learning material in memory stage
- To reproduce and recognize the learned information required.
- In memory level lower level of learning outcomes get focussed which includes learning facts and rules.
- Objective of teaching – To impart information or knowledge to students.
- social system – PUPIL AND TEACHER
- Support System – Oral, written and essay
- Emphasis/aims in-memory level means
- Organization of thoughts and ideas
- Systematic presentations to enable quick reproductions
- Mastery of correct sequencing of facts
- Facilitates recalling and recognizing of facts
- Reference:
Morrison‘s Model – Understanding Level:
- The learners are required to comprehend factual information
- To know the meaning of different concepts and their relationships.
- To apply facts, concepts and principles.
- Social system: teacher control the behavior of the pupil, pupil and teacher remain active in assimilation, pupil works with full involvement.
- Support system: pupil pass exam in presentation to enter into assimilation, to enter into organization and recitation, at the end written test is taken. Similarly recitation is followed by the oral test. Essay and objective type questions are asked.
- Understanding level of teaching propogates learning by Enhancing the scope for seeing of relationships and meanings.
- identifying examples of a given concept according to bloom’s taxonomy
- learning outcomes are intended in teaching by seeking of relationships and patterns among facts.
Set I (Steps of Morrison’s Teaching Model) Set II (Description of steps)
- Exploration – ascertaining the previous task-related behaviour of students
- Presentation – describing the theme to be taken up for discussion
- Assimilation – helping students to relate presented material to their internal self
- Organization – asking students to present their acquired ideas without help of teacher
- Recitation – revisiting the material.
Biggie and Hunt’s model – Reflective level of teaching:
- To develop insights into the learner to solve problems
- To develop rational and critical thinking in the students
- To develop the ability of independent thinking and decision making in the students.
- Objective – To develop problem solving competency, critical and constructive thinking and independent and original thinking.
- Syntax: steps;
- Creating a problematic situation.
- Formulation of the hypothesis.
- Verify hypothesis
- Collection of data.
- Testing of hypothesis.
- Social system: pupil occupies the primary place and teacher secondary place.
- Support system: Objective type test is not used but essay type test is used. Attitude, beliefs and involvement is evaluated
- Encourages critical thinking based cognitive interchange leads to analysis and creation
- Higher level learning outcomes like problem raising and problem-solving gets focussed.
Models of curriculum evaluation:
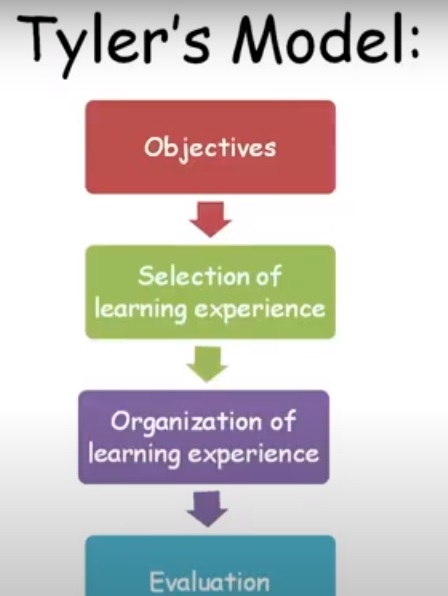
Tyler’s model of goal attainment:
- Selection of educational purposes
- Selection of learning experiences
- Organization of learning experiences
- Evaluation of learning experiences.
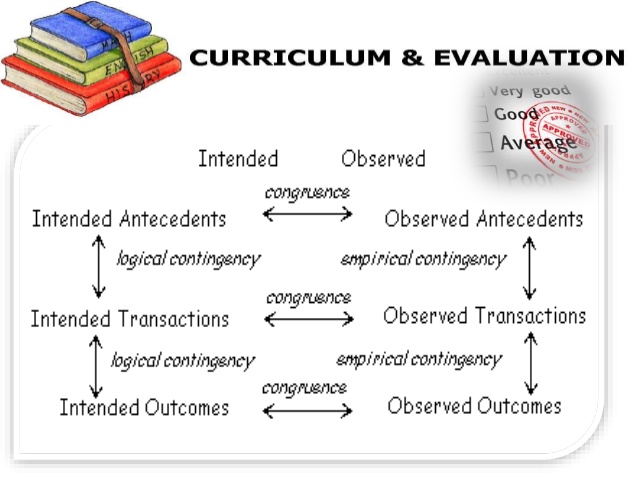
Stake’s model:
It lies in the manner in which intents and actions are defined, observed and evaluated together with standards and judgements rather than actual educational goals.
CIPP Model:
CIPP focused more on decision making at each stages of the curriculum processes.
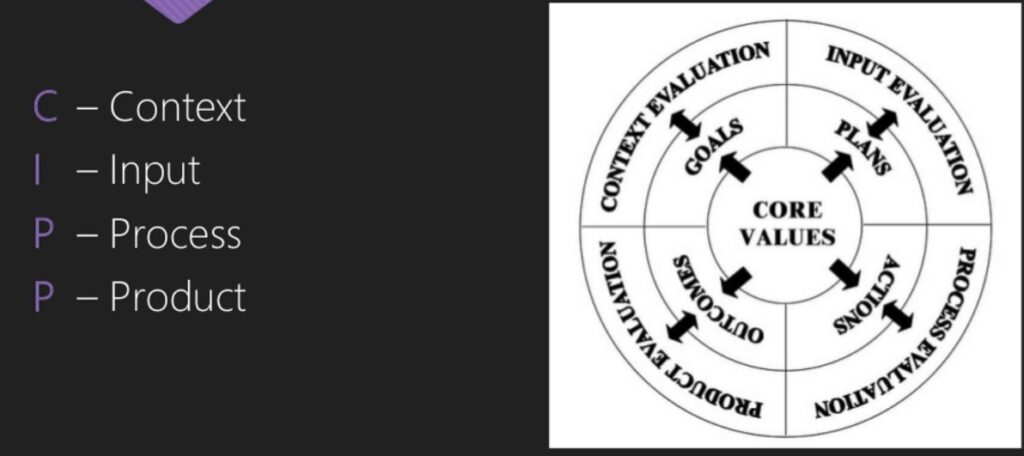
- List-I consists of types of evaluation in CIPP model while List-II comprises the objectives to be
achieved through these evaluation- List-I(Types of Evaluation) List-II Objectives
- Context evaluation – To determine the needs and opportunities present and diagnose the problems
- Input evaluation – To identify and assess the school system capacities
- Process evaluation – To identify defects in the procedural design or its implementation plan
- Product evaluation – To communicate information regarding objectives achieved and contents covered.
- List-I(Types of Evaluation) List-II Objectives
- the correct sequence of tasks involved in the development of curriculum
- Assessing needs
- Formulating goals and objectives
- Selecting and organising content
- Selecting appropriate instructional strategies
- Evaluating effectiveness of learning and instruction
Scriven’s model of evaluation:
- Formative assessment – During the process of curriculum development – identifies the scope and potential for improvement of students
- Teacher’s method of providing feedback and follow up action during instruction
- Extent of learning and motivation ensured by the teacher while teaching
- Management and mentoring technique employed by the teacher
- summative – At the end of curriculum judges the learning standards.
- Scriven’s formative model (1967) of curricular evaluation advocates for :
- Field traits of course materials
- Interacting with learner together
- Gather opinions by external group on course developmen
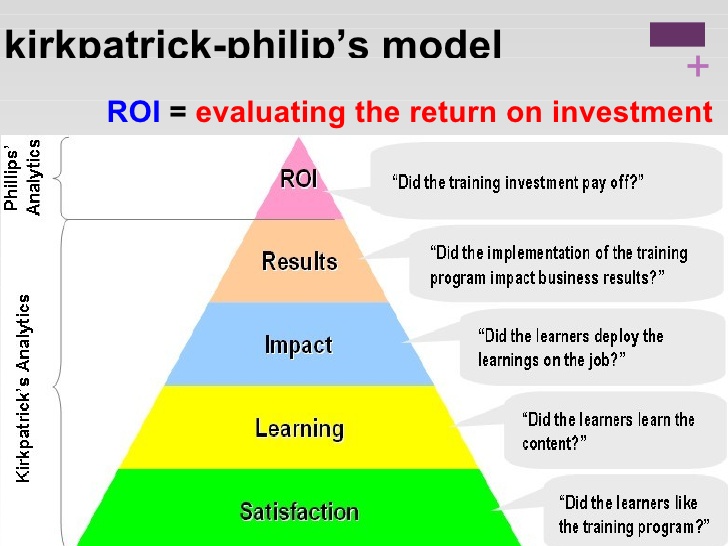
Kirkpatrick’s Model:


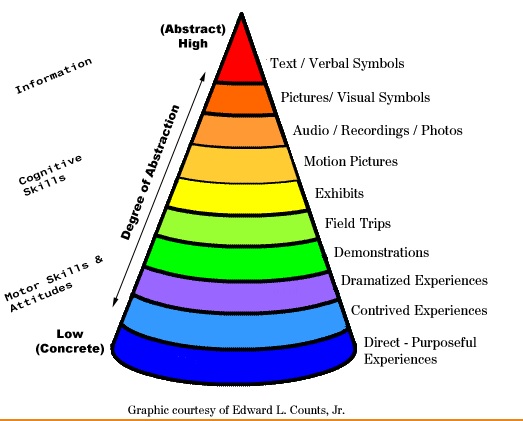
Experiential Learning:
Logic of learning Phenomena
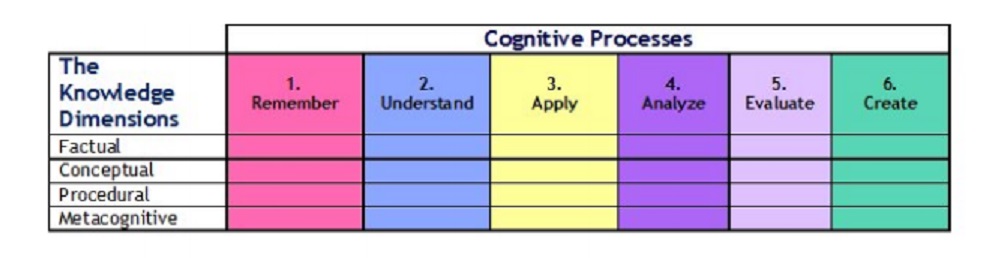
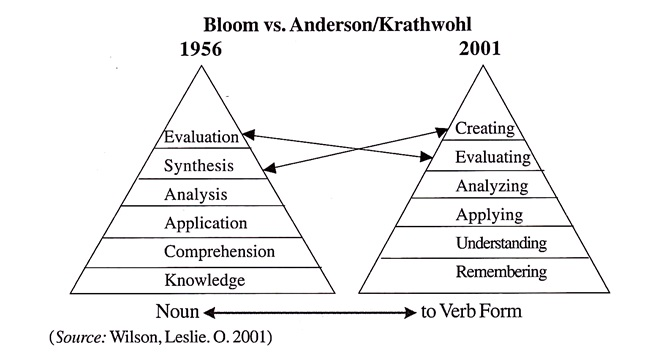
Anderson and Krathwohl are students of bloom: proposes revision of blooms taxonomy. Along with blooms taxonomy 4 th dimension added by the above scientist
- Factual – memory based
- Conceptual – Understaning
- Procedural – critical thinking
- Metacognitive – Meta-cognition involves self-awareness and control of cognitive abilitites eg. planning,reviewing and revising etc.
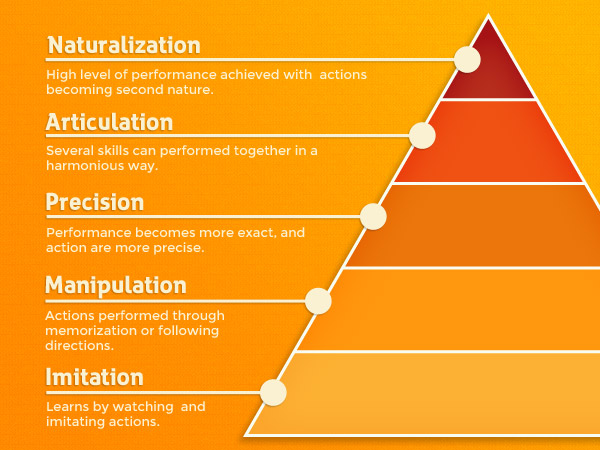
R.H. Dave – psychomotor domain of learning:
- There are 5 levels of skills
- Imitation – Learner watches actions of another person and imitates them.
- Manipulation – Learner performs actions by memory or by following directions
- Precision – Learner’s performance becomes more exact
- Articulation – Learner can perform several skills together in a harmonious manner.
- Naturalistion – Learner achieves high level of performance, and actions become natural with little or no thought about them.
Andragogy:
Malcolm knowles advocates adult learnning by the model of learner autonomy. It includes the following assumptions
- Self-concept
- Past learning experience
- readiness to learn
- Practical reasons to learn
- Driven by internal motivation
Assessments in andragogy:
Interaction analysis category System
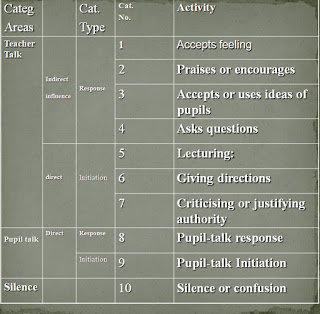
- The focus of the Ned Flanders interaction analysis categories system is on the study of verbal behaviour of students.
- In Flanders Interaction Analysis Categories (FIAC) the following are related to Indirect Teacher Talk (ITT). Indicators of indirectness in Flander’s interaction analysis
- Acceptance of feelings
- Praising or encouraging
- Using student’s ideas
- direct Teacher Talk indicators are
- Giving directions
- Lecturing
- Criticizing or justifying authority by the teacher
- On the basis of Flanders’ Interaction Analysis Categories (FIAC) in a 10 x 10 observation matrix, the cells which indicate a sustained level of verbal interchange are known as Steady State Ratio (SSR).
Galloway:
- the main assumption of charles Galloway system of observations
- Non-verbal communication can be more effective during interaction in the classroom
- In galloway system of interaction analysis there is recording of classroom events, construction and interpretation of interaction matrix.

- Portfolio test – They are measured on the basis of products and need global assessment.
- In Portfolio assessment, the priority is given to,
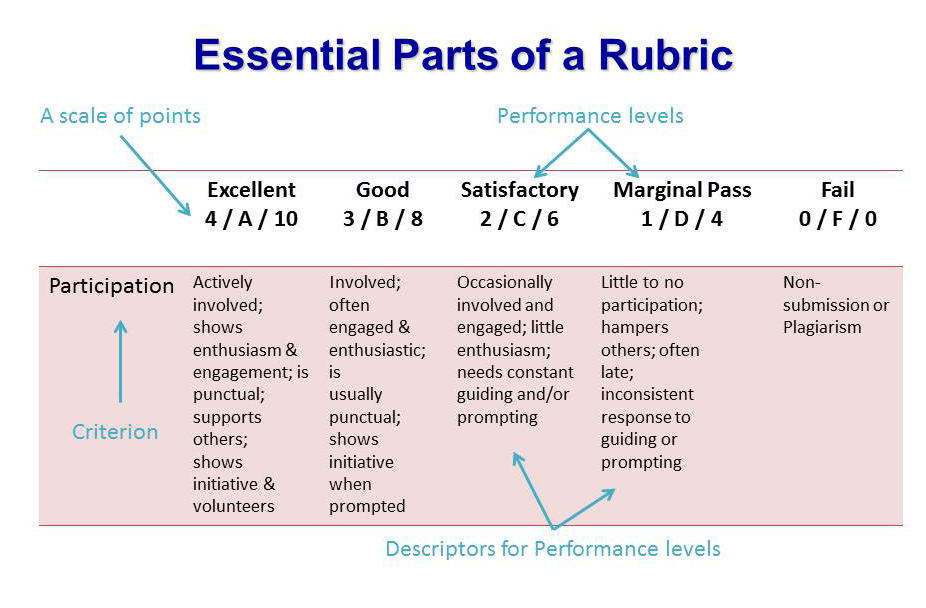
- The rubrics in terms of which Portfolio will be judged
- A rubric is a chart or matrix which includes indicators that describe different levels of achievement for the major components or ‘elements’ of a performance.
- Rubrics can be a powerful self-assessment tool—if teachers disconnect them from grades and give students time and support to revise their work.
- Here The Steps in Preparing Rubric are given
- Performance Objective
- Dimensions
- Gradation Levels
- Point Value
- Criteria
- Create Rubric
- Rubric is a set of criteria used for assessment
- A student’s score on Criterion Referenced Test is best used to provide information about student’s Mastery of a defined body of content.
- CRT is used to ascertain an individuals achievement status with respect a well defined specific behaviour objectives.
- Bench marking will be the preferred measurement indicator of Criterion Referenced Test (CRT)
Recent Comments